0% found this document useful (0 votes)
394 views10 pagesTransformer Fire Protection System
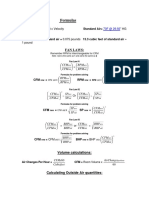
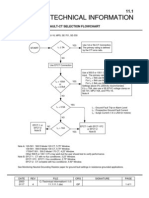
The document discusses the risks and causes of transformer fires, emphasizing the importance of fire protection systems due to the potential for significant damage. It outlines various causes of transformer fires, including overheating and electrical issues, and details fire protection requirements and extinguishing methods. Additionally, it describes the components of a fire protection system and the advantages of implementing such systems.
Uploaded by
Tuhafeni HailekaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
394 views10 pagesTransformer Fire Protection System
The document discusses the risks and causes of transformer fires, emphasizing the importance of fire protection systems due to the potential for significant damage. It outlines various causes of transformer fires, including overheating and electrical issues, and details fire protection requirements and extinguishing methods. Additionally, it describes the components of a fire protection system and the advantages of implementing such systems.
Uploaded by
Tuhafeni HailekaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10