FOOT VALVE
ENGR. SYED SAAD ALI
www.linkedin.com/in/engrsyedsaadali
� What is a Foot Valve?
It’s Working, Types, and Applications
Foot Valve vs Check Valve
A foot valve is a special type of non-return valve, with a strainer affixed to the open end. For suction lift
applications, foot valves are widely used in the pump suction or at the bottom of pipelines. The use of foot
valves, keeps the pump primed, the fluid flows in but does not flow back out, and hence they are ideal for
wells, ponds, and pools. As the flow area of the foot valves is larger than the pipe size, there is very less head
loss.
ENGR. SYED SAAD ALI
Working of a Foot Valve
Foot valves being unidirectional allow the flow only in one direction and the valve closes for reverse flow. The
inlet strainer of the foot valve filters out the unnecessary solid particles from the fluid and thus prevents valve
damage.
When pumps are used to move fluids from lower to higher elevations, a lot of energy will be required. At the
same time when the pump is turned off, the liquid will flow back to the lower level. But the use of foot valves
prevents this reverse flow. The foot valve maintains the liquid column even when the pump is not working.
Foot valves are basically a type of check valve that prevents the backflow of liquid. They are placed in the
pick-up end of the pipe and are located at the very bottom. When the pump is started, a suction is created
which opens the foot valve. Water or other liquid easily enters the pipe through the foot valve due to the
pulling force of the pump. But when the pump is turned off, this pulling force is removed but still, the water
level retains its level as the foot valve does not allow the water to flow back. thus the pump remains always
primed.
Requirements for Foot Valves
Foot valves are used for various reasons like:
www.linkedin.com/in/engrsyedsaadali
� To keep the pump primed when pumping liquid from lower to higher levels.
To prevent damage to water pumps without foot valves there may be dry runs. Without a foot valve, the
air will fill the pipe which will oppose the water flow and the pump will run dry.
To reduce energy wastage.
Functions of the Strainer for the Foot Valve
The strainer in a foot valve filters out the debris that may jam the foot valve and can cause damage to the
pump. So, the strainers protect the valves and pumps and perform a very important function.
ENGR. SYED SAAD ALI
Features of a Foot Valve
Foot valves usually have self-tapping male and female threads that help in easy installation. They have
internal balls for quick sealing and valve reaction. They are flexible enough to fit various types of water pump
uses. Foot valves are cheaper compared to other valves.
Components of Foot Valves
Each foot valve consists of 4 basic components:
Screen: To remove sediments or debris.
Body: The complete mechanism is housed within the valve body.
Seat: The seat is an integral part of the body and uses o-rings to avoid leakage when the valve is
closed. The valve lands on the seat when the pump is turned off.
Disc: This is the gateway of the foot valve. When the disc is raised, liquid can enter.
Materials for Foot Valves
Foot valves are usually constructed of heavy-duty cast iron, bronze, Stainless Steel, PVC, and Plastic. Foot
valves are normally used for water services and these materials last longer when submerged in water.
www.linkedin.com/in/engrsyedsaadali
� Applications of Foot Valves
As foot valves prevent the suction column from draining when the pump is not in operation, they are widely
used in all kinds of pneumatic systems. The major application of foot valves is found in pumps and because of
that, they are sometimes called foot valves for pumps or well-pump foot valves. Typical applications
of foot valves include:
Suction lines of the pipeline
Ponds, pools, and wells, where pumps are used to transfer water.
Sump pumps, and intake pumps, in rivers and lakes.
ENGR. SYED SAAD ALI
Pneumatic brake lines of commercial trucks.
Car wash systems.
Irrigation systems.
Rural fire protection systems.
HVAC systems.
Types of Foot Valves
Foot valves can be classified based on construction and flow systems. Based on the construction of foot
valves, there are two types of foot valves, Membrane foot valve, and ball foot valve.
Membrane foot valve: In a membrane foot valve, a cylindrical rubber membrane is fitted inside a steel
strainer. When the suction is formed in the strainer, the membrane is displaced and the liquid flows through
the valve. The cylindrical membrane closes during a reverse flow and thus prevents the backflow.
Ball foot valve: In this type of foot valve, a cylindrical inclined chamber and seating have used that guide
the ball valve. When inward flow occurs, the ball is displaced with its chamber, and fluid flows. On the other
hand, when the flow rate decreases, it runs down the chamber onto its seat and the valve prevents reverse
flow. Ball foot valves are mostly used for contaminated water.
www.linkedin.com/in/engrsyedsaadali
� According to the flow system, the foot valves are classified as Microflow system valves, high-flow system
valves, and low-flow system valves.
The microflow system valves are mostly made of stainless steel and used in direct push technology
micro-wells and multilevel good installation.
The high-flow system valves are used on 2-inch wells or larger and can stand high pumping rates and
very deep wells.
The low-flow system valves are used in small diameter piezometers which lift up to 100 feet of water.
Based on the types of threads used, foot valves are of three types:
ENGR. SYED SAAD ALI
Female threaded foot valve.
Male threaded foot valve
Dual-threaded foot valve
Selection of Foot Valves
Foot valves are selected considering various parameters like:
The task that the foot valve will perform and fluid service.
Duty of valve; whether heavy-duty or light-duty.
Load the foot valve need to carry.
Durability.
Maintaining a Foot Valve
Even though a foot valve is a small element, it must be properly maintained. Some of the steps that can be
followed to increase the life of foot valves are:
Regular cleaning of debris of the foot valve.
Regular checking of corrosion signs.
Ensuring that the tank or well bottom is clean
www.linkedin.com/in/engrsyedsaadali
� Difference between Foot Valve and Check Valve
Even though both the check valve and foot valve serves a similar function of a non-return valve i.e, preventing
backflow, there are some distinct differences between the two valves. They are:
Foot Valve Check Valve
The foot valve has a strainer affixed to the valve The check valve does not have a strainer.
Foot valves are installed at the suction side of the Check valves are installed at the discharge side of the
pump. pumps.
Foot valves have only one thread for installation. Check valves have threads on both ends.
ENGR. SYED SAAD ALI
Foot valves can be installed only at the end of the
Check valves can be installed in the middle of pipes.
pipe.
The use of foot valves is limited to pump lines
Check valves have multiple uses.
only.
www.linkedin.com/in/engrsyedsaadali
� IMPORTANT INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
It is very important to install a Foot Valve in a vertical position to help insure a trouble free operation.
A. Pipe Flow Velocities: High flow- When selecting a foot valve insures that the valve is sized properly to flows
normally not to exceed 5 feet per second. Too high of a flow can create cavitation of the pump resulting in
efficient operation and potential premature failure. Industry practice is to use one size larger suction pipe than
pump discharge pipe size. If pump discharge is 1” use a minimum 1 ¼” suction pipe and foot valve. If pump
discharge pipe is 6” use an 8” suction pipe and foot valve etc. Low flow- conditions below 2 feet per second is not
recommended as it can cause premature wear on the internal foot valve poppet parts. It is important that the foot
valve is sized for the proper flow conditions and not the pipe size.
B. System pressure: It is important to take the total system hydraulics into the calculation and not only the pumps
well setting when selecting valve type and model. In general Flomatic valves are pressure rated 400 psi or 920 feet
of water pressure. This does not mean that a valve can be set at a well depth of 920 feet. To alleviate and reduce
the hydraulic shocks in the riser pipe it is recommended that a check valve be installed every 200 feet in the riser
pipe. See Recommend Check Valve Installation chart below.
C. Prior to installing foot check valve: Make sure well has been pumped clean. Make sure that the foot valve is
free from defects and that the valve’s spring-loaded poppet mechanism is operating freely. Remove any foreign
ENGR. SYED SAAD ALI
material from valve seat.
D. Install foot check valve vertically with arrow pointed up in direction of liquid flow. The foot valve shall be installed
a maximum of 25 feet vertical distance below the suction pipe of the pump inlet. The foot valve screen shall not be
supported at the bottom of tank or well for best operation efficiencies. In addition the foot valve screen shall be a
minimum .75 times the pipe diameter (i.e. 6” valve x 0.75 = 4.5”), below the minimum water pumping level. This
will insure minimum submersion to avoid suction vortex.
Foot Valve Location Recommended Foot Valve Installation:
Max. 25 feet or less below Install Foot Valve in a vertical position for best and most
pump suction inlet efficient operation.
WELL CASING
RISER PIPE
FOOT VALVE
www.linkedin.com/in/engrsyedsaadali
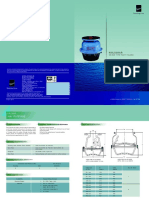
� FOOT VALVE
OVERALL DIMENSIONS
ENGR. SYED SAAD ALI
1/2" 3/4" 1" 1"1/4 1"1/2 2" 2"1/2 3" 4"
DN 15 20 25 32 40 50 65 80 100
A 68,5 84,5 99 113,5 122,5 142,5 168 194,5 216,5
B 39 45 51 61 68,5 80 100 121 145
Kg/cm2 bar 10 10 10 8 8 8 6 6 6
LBS - psi 145 145 145 116 116 116 87 87 87
MATERIALS
POS. DESCRIPTION N. MATERIAL
1 Body 1 Brass CW617N
2 Plate 1 Brass CW617N
3 Washer 1 NBR
4 Washer 1 Fiber
5 Ring 1 Brass CW617N
6 Cartridge 1