IGCSE ICT Input & Output devices 0417
Unit 2 – Input & Output Devices
Alphanumeric Keyboard
A very common, general purpose, input device that allows text (abc…), numbers (123…) and symbols
(%$@...) to be entered into a computer.
A keyboard is simply a set of buttons. Each button has a symbol assigned
Numeric Keypad
A small keyboard that only has numbers.
Used to enter numeric data into computers such as those in ATMs.
Most computer keyboards have a numeric keypad on the right side, and most mobile phones (there are also
computers) have a one for entering phone numbers, etc.
PIN Pad
This is a device with a numeric keypad used to enter a person’s Personal Identity Number (PIN) e.g. when
paying with a credit card.
PIN pads are also found on electronic door locks – you enter a PIN to unlock the door.
Mouse
A pointing device found on most PCs. Sensors on the bottom of the mouse detect when the mouse is moved. Data
about this movement is sent to the computer. Often used to control the pointer in a GUI. Using a mouse the user can
select an icon, open an application, scroll windows, switch between windows etc.
Touchpad / Trackpad
A pointing device found on most laptops. Used instead of a mouse since it takes up less space. The user moves a
finger across the touch pad and this movement data is sent to the computer. Usually used to control the pointer in a
GUI.
Trackball / Tracker Ball
This pointing device is not moved about like a mouse, instead it has a large ball that the user spins. Data
about which direction the ball is spun is passed to the computer.
It can be used to control a GUI pointer.
Tracker balls are often used by people with limited movement (disabled) or by the very young since they are
easier to use than a mouse.
Touch Screen
A touch screen is an alternative to a separate pointing device. With a touch screen the user selects items on the
screen by touching the surface. This makes touch screen systems very intuitive and simple to use.
Often used for information terminals in public places e.g. libraries or museums where mice or keyboards
may be stolen or damaged.
Because they are so intuitive to use, and now they are getting cheaper to manufacture, touch screens will probably
become the most common hardware interface for our electronic gadgets.
Graphics Tablet
A pointing device often used by designers and artists to allow natural hand movements to be input to graphics
applications. A stylus is held like a pen and moved over the surface of the tablet. Data about the stylus movements are
sent to the computer. Since it is so like using a pen, it is very easy to create ‘hand-drawn’ sketches.
Joystick / Joypad
Used mainly for playing games. The user moves the joystick left/right, forward/back and data about these movements
are sent to the computer. Small joysticks can also be found on some mobile phones.
6
�IGCSE ICT Input & Output devices 0417
Light Pen
A light pen is a device used as a pointing device or to ‘write’ on the screen of a computer. Light pens are rarely
used today since graphics tablets and high-quality touch screens provide similar functionality.
Scanner
A device that ‘scans’ images, book pages. Taking a close-up photograph and storing in a secondary storage
device of the computer. Flat-bed scanner which has a glass plate on which the item to be scanned is placed.
The item is illuminated and an image of it is captured by a moving scan ‘head’.
Digital Camera
A device that captures digital photographs.
Most digital cameras do not directly input data into a computer - they store photographs on memory cards.
The photographs can later be transferred to a computer.
A modern digital camera can capture 10-16 Megapixels or more per photograph - that’s 10,000,000 coloured
dots (pixels) in every photo!
Video Camera
A device that captures moving images, or video.
Like a digital camera, most video cameras do not directly input data into a computer – the captured movies are
stored on video-tape or memory cards and later transferred to a computer.
However, there are some situations where video cameras do feed video data directly into a computer:
television production and video-conferencing. In these situations the video data is required in real-time.
Web Cam
This is a very basic video camera used to feed live video into a computer.
The video data from a web cam is low quality compared to a full video camera. However it is good enough
for web chats (e.g. using a messenger application such as MSN Messenger or Skype).
Usually a web cam is clipped to the top of a monitor, but many laptops now have web cams built into the edge
of the screen.
Microphone
An input device that converts sound into a signal that can be fed into a computer which is analogue so, before
it can be processed by a computer, it must be converted into digital data. An Analogue-to-Digital Convertor
(ADC) is used for this (usually built into the computer’s sound card)
Many headphones now come with microphones to allow them to be used with chat and phone applications
Direct data entry and associated devices:
Magnetic Strip Reader
Many plastic cards, such as credit cards, have a strip of magnetic material on the back of the card. Data can
be stored here in the form of magnetised dots.
The card usually stores the card number, expiry date, card type & security pin.
The stripe allows this data to be input to a computer system faster and more accurately than by typing it in.
A magnetic strip/stripe reader is used to read the data from the stripe. This is usually done by ‘swiping’ the
card through a slot on the reader.
Smart Card / 'Chip' Reader
Modern credit cards and ID cards don’t use a magnetic strip. Instead they have a tiny ‘chip’ of computer
memory embedded inside them.
Data can be stored in this memory and read back using a ‘chip’ reader.
Smart cards can store much more data than magnetic strip cards, e.g. an ID smart card would store not only
the owner’s name and card number, but might also have a digital image of the person.
Many types of card use this system: id cards, phone cards, credit cards, door security cards, etc.
7
�IGCSE ICT Input & Output devices 0417
MICR Reader
Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR) is a technology
that allows details from bank cheques to be read into a computer
quickly and accurately.
The cheque number and bank account number are printed at the
bottom of each bank cheque in special magnetic ink using a special font. These numbers can be detected by
an MICR reader.
OMR Scanner
Optical Mark Recognition (OMR) is a technology that allows the data from a multiple-choice type form to
be read quickly and accurately into a computer.
Special OMR forms are used which have spaces that can be coloured in (usually using a pencil). These
marks can then be detected by an OMR scanner.
Common uses of OMR are multiple-choice exam answer sheets and lottery number forms.
OCR Scanner
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is a software technology that can convert images of text into an
actual text file that can then be edited, e.g. using word-processing software). The result is just as if the text
had been typed in by hand.
OCR is typically used after a page of a book has been scanned. The scanned image of the page is then
analysed by the OCR software which looks for recognisable letter shapes and generates a matching text file.
Advanced OCR software can recognise normal handwriting as well as printed text - this is usually called
handwriting recognition.
Barcode Reader / Scanner
A barcode is simply a numeric code represented as a series of lines. These are read by a barcode
reader/scanner.
The most common use of barcode readers is at Point-of-Sale (POS) in a shop. The code for each item to be
purchased needs to be entered into the computer. Reading the barcode is far quicker and more accurate than
typing in each code using a keypad.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) readers :
Automatically identifying and tracking tags attached to objects. The tag does not necessarily need to be
within line of sight of the reader and may be embedded in the tracked object.
Automatic number plate recognition (ANPR) is a mass surveillance (observation) method that uses
optical character recognition on images to read vehicle registration plates. They can use existing road-rule
enforcement cameras as a method of electronic toll collection on pay-per-use roads and cataloging the
movements of traffic.
ANPR can be used to store the images captured by the cameras as well as the text from the license plate,
with some configurable to store a photograph of the driver. Systems commonly use infrared lighting to allow
the camera to take the picture at any time of the day.
Input – Sensors : A sensor is a device that converts a real-world property (e.g. temperature) into data that a
computer can process.
Sensor What it Detects
Temperature Temperature
Light Light / dark
Pressure Pressure (e.g. someone standing on it)
Moisture Dampness / dryness
Water-level How full / empty a container is
Movement Movement nearby
Proximity How close / far something is
Switch or button If something is touching / pressing it
8
�IGCSE ICT Input & Output devices 0417
Input - Remote Control
These devices are very common. They send data signals each time a button is pressed using infrared light or radio
signals. The signals can control a computer (or a system that contains a small computer such as a DVD player) from
some distance. Often used to control a presentation slideshow.
Computers are used to manage data every organization. Name different methods used to input data.
1. Type in/use keyboard - Any data in the form of numbers, text & special characters can be typed in.
But... Takes a long time and can contain errors.
2. Use touch screen – A user can give input or control the information processing system through
simple or multi-touch gestures by touching the screen with a special pen and or by fingers. It does not
require special input or output device But.. only limited amount of data can be typed in.
3. Scan Bar code / use bar code reader - An electronic device that can read and output printed
barcodes to a computer. Only barcodes can be read from products or devices.
4. Swipe Magnetic stripe or magnetic stripe reader – is a device that reads the information encoded
in the magnetic stripe located on the back of a plastic badge to input the customer bank information.
This magnetic layer can be damaged by magnetic field or inappropriate use of the card. (even can be
stolen)
5. Biometric method – Reads human characteristic which is unique for each individual and compares
with the data (image) stored in the database. It is very accurate but it takes a long time to record
individual information. .
6. OMR – Optical mark recognition also called optical mark reading is the process of capturing human-
marked data from document forms such as surveys and tests. Pencil marks are read and compared
against what is stored in the database. Quick and easy method to input data but only pencil marks.
Cannot be used to read text.
7. OCR – To scan printed text into machine-encoded text. It is widely used as a form of data entry from
printed paper data records, whether passport documents, invoices, bank statements, computerized
receipts, business cards, mail, printouts of static-data, or any suitable documentation. It is a common
method of digitizing printed texts so that it can be electronically edited, searched, stored more
compactly, displayed on-line, and used in machine processes such as machine translation or text-to-
speech. May not identify all handwritten documents.
8. Chip reader - adopted by the banking industries for credit, debit, and ATM cards. It is an alternative
implementation that requires the cardholder to verify identity by signing a printed receipt rather than
entering a PIN
Output Devices:
A soft copy is available on a computer. User can edit, modify or transfer. Can save on the disc for later use
while the hard copy is printed on the paper. Once printed cannot be changed.
CRT Monitor
A monitor displays text and image data passed to it by the computer.
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) monitor is the type that has been around for years and is large and boxy.
CRT monitors are heavy and they take up a lot of desk space.
They have largely been replaced by flat-screen monitors. However some are still used in the design industry
since the colour accuracy and brightness of CRT monitors is excellent, and designers need to see true-to-life
colours & the monitors are generally cheaper than flat-screen monitors.
Flat-Screen Monitor (TFT or LCD) - They are light in weight and they take up very little desk space. They
have a better picture quality. TFT is Thin-Film-Transistor, and LCD is Liquid-Crystal Display.
9
�IGCSE ICT Input & Output devices 0417
TFT/LCD monitor (Thin Film Transistor / Liquid crystal display) : They are compact, light weight, high
degree of visual comfort, image remains perfectly stable and clear, low power consumption and heat release
is very low but very high resolutions are not as readily available for professional applications.
TN Monitors (Twisted Nematic)
Molecules in the liquid align themselves into a threadlike shape. Nematic liquid crystals are used in
twisted nematic display s, the most common form of liquid crystal display.
Most common desktop computers have TN monitors.
It is comparatively cheap to produce panels based on this technology
Higher resolutions
Commonly used for gaming screens since they have fast response time.
But ... Most restrictive viewing angles, especially in vertical plane.
IPS /LCD monitor (In-plane switching) is a screen technology used for liquid crystal displays (LCDs).
It displays consistent, accurate color from all viewing angles.
IPS panels do not lighten or show tailing when touched. This is important for touch-screen devices, such as
smart phones and tablets.
They offer clear images and stable response time
LED display is a flat panel display, which uses an array of light-emitting diodes as pixels for a video display. Their
brightness allows them to be used outdoors in store signs and billboards, and in recent years they have also become
commonly used in destination signs on public transport vehicles. LED displays are capable of providing general
illumination in addition to visual display, as when used for stage lighting or other decorative (as opposed to
informational) purposes.
Digital / Multimedia Projector
Digital projectors are used in situations when a very large viewing area is required, for example during
presentations, for advertising, or in your home for watching movies.
A projector connects to a computer, a DVD player or a satellite receiver just like a ordinary monitor.
The image is produced inside the device and then projected out through a large lens, using a powerful light
source.
Loudspeaker - To hear music or sounds from your computer, you will have to attach loudspeakers. They convert
electrical signals into sound waves. Loudspeakers are essential for applications such as music editing, video
conferencing, watching movies, etc.
Dot Matrix Printer
A dot-matrix printer is named after the pattern (a grid or ‘matrix’) of dots used when creating the
paper printout.
These dots are formed by tiny pins in the printer’s print head that hit an inked ribbon against the
paper leaving marks. As the print head moves along it leaves a pattern of dots behind it which can
form letters, images, etc.
Dot matrix printers often use continuous stationary: long, continuous strips of paper (rather than separate
sheets of A4 like ink-jet and laser printers use).
After printing, the printout is torn off from the long strip.
Dot-matrix print quality is poor, the printers are noisy, and there are much better printing systems
available today. Since the pins actually hit the paper, several ‘carbon-copies’ can be printed in one
go. The print mechanism is very cheap, and the inked ribbons last for a long time. So, where cheap,
low-quality printouts are required, dot-matrix printers are used. An example is shop receipts.
10
�IGCSE ICT Input & Output devices 0417
Ink Jet Printer
Cheap, high-quality, full-colour printing became available during the 1980s due to the development of ink-
jet printers.
These printers have a similar print-head mechanism to a dot-matrix printer. The print-head passes left and
right across the paper. However, instead of using pins to hit inky marks onto the paper, the ink-jet squirts tiny
droplets of ink onto the surface of the paper. Several coloured inks can be used to produce full-colour
printouts.
The droplets of ink come from tiny holes (the jets) which are less than the width of a human hair in size. Each
droplet creates a tiny dot on the paper. Since the dots are so small, the quality of the printout is excellent (1200
dots-per-inch are possible). This is perfect for photographs.
Ink-jet printers are very quiet in use. Since they have so few moving parts they are also cheap to manufacture
and thus cheap to purchase. However, the ink is very expensive to buy (this is how the printer companies
make their profits!) so the printers are expensive to use.
Laser Printer
Laser printers are very complex devices, and thus expensive to buy. However they are very cheap to use.
This is because they produce marks on paper using a fine dust called toner which is relatively cheap to buy. A
single toner cartridge will often last for 5,000-10,000 pages of printing.
The laser printer uses a complex system, involving a laser, to make the toner stick to the required parts of the
paper. (This system is very different to a dot-matrix or ink-jet, and you don’t need to know the details.)
The laser and toner system allows very fast printing compared to other printers (just a few seconds per page).
Laser printers are very common in offices since they print very quickly, are cheap to use and are reasonably
quiet.
Wide format printer:
These are generally accepted to be any computer-controlled printing machines that support a maximum print
roll width of between 18" and 100".
These are used to print banners, posters, trade show graphics, wallpaper, murals(wall painting), backlit
film(looks like lit in darkness), vehicle image wraps, electronic circuit schematics, architectural drawings,
construction plans, backdrops for theatrical and media sets, and any other large format artwork or signage.
They are more economical than other print methods such as screen printing for most low quantity print
projects, depending on print size, run length (quantity of prints per single original), and the type of substrate or
print medium.
Wide format printers are usually designed for printing onto a roll of print media that feeds incrementally
during the print process, rather than onto individual sheets.
3D printer: It is used to make a three-dimensional object. In 3D printing, successive layers of material are laid down
under computer control. These objects can be of almost any shape or geometry, and are produced from a 3D model or
other electronic data source.
Plotter: Plotters draw on the paper using a pen. The pens are held in an arm which can lift the pen up or
down, and which can move across the paper. The arm and pen create a drawing just like a human could, but
much more accurately and more quickly. Different coloured pens can be used to produce coloured line
drawings. Plotters are used by designers and architects to work with huge pieces of paper (A0 paper size),
far bigger than anything a normal printer could work with.
11
�IGCSE ICT Input & Output devices 0417
Output - Control Actuators
A normal PC has no muscles, but we can give it some. In fact we can give it the ability to do lots of things by
connecting a range of actuators to it…
An actuator is a device, controlled by a computer, that can affect the real-world.
Actuator What it Can Do
Light bulb or LED Creates light
Heater Increases temperature
Cooling Unit Decreases temperature
Motor Spins things around
Pump Pushes water / air through pipes
Buzzer / Bell / Siren Creates noise
Motor- Motors can provide movement. For example, the motor in a washing machine can be controlled by a
computer - it is switched on when the clothes are loaded for washing and switched off at the end of the wash.
Computer-controlled motors are also found in microwave ovens (to turn the food around) and air-
conditioning units.
Pumps - A pump is basically a motor attached to a device that can push water or air along pipes. When the motor is
switched on, water or air flows along the pipes to places it is needed. Pumps are used in many places: as
part of watering systems in greenhouses, in factories, etc.
Buzzer - Buzzers can provide noise. For example, the buzzer in a microwave oven can be switched on by the
controlling computer when the food is cooked. Louder noises can be made using a siren or an electric bell,
for example in a burglar alarm system.
Lights - Lightbulbs and LEDs can by used to provide light, or to indicate something. For example,
computer-controlled lights are used in traffic lights, at music concerts. Lights are used in car
dashboards to show if the any of the systems in the car have problems.
Heaters / Coolers
Heaters can provide heat, and coolers can cool things down.
A computer can switch a heater on or off when needed to keep a room or a greenhouse at the correct
temperature during winter.
A computer can switch a cooling unit on or off to keep a room at the correct temperature during hot
weather, or to keep food fresh.
Revision:
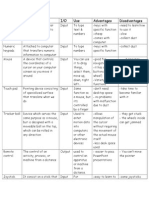
1.. Fill in the blanks with suitable hardware to complete the following statements:
a) Inputting freehand drawings into a computer ………………………
b) Operating a television ………………………
c) Entering text when writing a book ………………………
d) Selecting options in a tourist information kiosk ………………………
e) Reading information from a credit card ………………………
f) Inputting voiceovers into presentation software ………………………
g) Selecting options from a list ………………………
h) Inputting a PIN at an ATM ………………………
i) Inputting data from a school register ………………………
j) Inputting code numbers from products at a POS terminal ……………………
12