0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views9 pagesC2 Self Test (Cell Structure and Function)
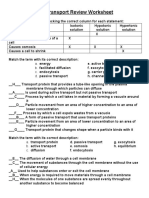
The document is a self-test review on plant cell structure, function, and transport mechanisms. It includes vocabulary definitions, multiple-choice questions, and true/false statements related to cell biology concepts such as osmosis, active transport, and cellular organelles. The test aims to assess understanding of key terms and processes in cellular biology.
Uploaded by
ryzap1Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views9 pagesC2 Self Test (Cell Structure and Function)
The document is a self-test review on plant cell structure, function, and transport mechanisms. It includes vocabulary definitions, multiple-choice questions, and true/false statements related to cell biology concepts such as osmosis, active transport, and cellular organelles. The test aims to assess understanding of key terms and processes in cellular biology.
Uploaded by
ryzap1Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 9