LEARN ABOUT
SEARCH
Search ASQ...
QUALITY
Magazines and Journals search (/quality-
resources/pub/search)
THE DEFINE MEASURE ANALYZE
IMPROVE CONTROL (DMAIC)
PROCESS
Quality Glossary Definition: DMAIC (/quality-resources/quality-glossary/d#dmaic)
DMAIC is a data-driven quality strategy used to improve processes. It is an integral part of a Six Sigma (/quality-resources/six-sigma) initiative, but
in general can be implemented as a standalone quality improvement procedure or as part of other process improvement initiatives such as lean
(/quality-resources/lean).
WHAT DOES DMAIC STAND FOR?
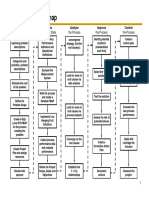
DMAIC is an acronym that stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It represents the five
phases that make up the process:
1. Define the problem, improvement activity, opportunity for improvement, the project goals, and customer
(internal and external) requirements.
• Project charter to define the focus, scope, direction, and motivation for the improvement
team
• Voice of the customer to understand feedback from current and future customers
indicating offerings that satisfy, delight, and dissatisfy them
• Value stream map (/quality-resources/lean/value-stream-mapping) to provide an overview
of an entire process, starting and finishing at the customer, and analyzing what is required to meet
customer needs
2. Measure process performance.
• Process map for recording the activities performed as part of a process
• Capability analysis (/quality-resources/process-capability) to assess the ability of a process to meet specifications
• Pareto chart (/quality-resources/pareto) to analyze the frequency of problems or causes
3. Analyze the process to determine root causes of variation, poor performance (defects).
• Root cause analysis (/quality-resources/root-cause-analysis) (RCA) to uncover causes
• Failure mode and effects analysis (/quality-resources/fmea) (FMEA) for identifying possible product, service, and process
failures
• Multi-vari chart (/quality-progress/articles/case-studies/the-multi-vari-chart-an-underutilized-quality-tool?
id=d23574b44b3d49b88e9dcdddc4785cbb) to detect different types of variation within a process
4. Improve process performance by addressing and eliminating the root causes.
• Design of experiments (/quality-resources/design-of-experiments) (DOE) to solve problems from complex processes or
systems where there are many factors influencing the outcome and where it is impossible to isolate one factor or variable from the
others
� • Kaizen event (/quality-progress/articles/lean-lessons-the-benefits-of-kaizen-and-kaizen-events?
id=eba923ad72c04eda9c579ffe2d543ffb) to introduce rapid change by focusing on a narrow project and using the ideas and motivation
of the people who do the work
5. Control the improved process and future process performance.
• Control plan (/quality-resources/quality-plans) to document what is needed to keep an improved process at its current level
• Statistical process control (/quality-resources/statistical-process-control) (SPC) for monitoring process behavior
• 5S (/quality-resources/lean/five-s-tutorial) to create a workplace suited for visual control
• Mistake proofing (/quality-resources/mistake-proofing) (poka-yoke) to make errors impossible or immediately detectable
DMAIC VS. DMADV
DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify) is a data-driven quality strategy that focuses on the development of new products or
services compared to existing ones. The DMADV method or approach is often used when implementing new strategies because of its basis in
data, its ability to identify success early, and its method, which requires thorough analysis. Like DMAIC, it is an integral part of a Six Sigma quality
initiative.
READ MORE ABOUT DMAIC
To DMAIC or Not To DMAIC? (/quality-progress/articles/back-to-basics-to-dmaic-or-not-to-dmaic?id=4494f067ddb040349ba07af1d03efe29) Identify
when you need a structured method for problem solving.
DMAIC Failure Modes (/quality-resources/articles/dmaic-failure-modes?id=7aa2451b82cd4936aa8d5328f21b6671) (ASQ member exclusive) Read
about actual experiences related to some of the key failure modes associated with DMAIC and effective countermeasures you can take.
How to Scope DMAIC Projects (/quality-progress/articles/how-to-scope-dmaic-projects?id=9625e846eabc408895db72be72695e71) (ASQ member
exclusive) Scoping is a vital part of the define phase and can have a long-term impact on a Six Sigma program’s ultimate success.
Excerpted from The Certified Quality Engineer Handbook (https://asq.org/quality-press/display-item?
item=H1602&utm_source=laq&utm_medium=webpage&utm_campaign=dmaic&utm_id=dmaic), (https://asq.org/quality-press/display-item?
item=H1602&utm_source=laq&utm_medium=webpage&utm_campaign=dmaic&utm_id=dmaic) ASQ Quality Press.
Featured Advertisers