0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views30 pagesInteractive Session 2-Cloud Computing
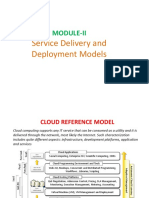
The document outlines an interaction session on Cloud Computing led by Mainak Chakraborty at IIT Delhi, covering various topics including deployment models, virtualization, XML, and web services. It emphasizes the importance of on-demand resource delivery, pay-as-you-go pricing, and the flexibility of cloud services. Additionally, it introduces key concepts such as IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, and provides insights into AWS services like EC2, S3, and Lambda.
Uploaded by
Ronak BhawnaniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views30 pagesInteractive Session 2-Cloud Computing
The document outlines an interaction session on Cloud Computing led by Mainak Chakraborty at IIT Delhi, covering various topics including deployment models, virtualization, XML, and web services. It emphasizes the importance of on-demand resource delivery, pay-as-you-go pricing, and the flexibility of cloud services. Additionally, it introduces key concepts such as IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, and provides insights into AWS services like EC2, S3, and Lambda.
Uploaded by
Ronak BhawnaniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 30