1
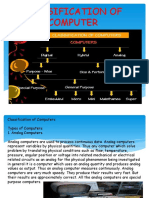
COMPUTER:
Computer is an electronic machine that receives data as input, process the data and provides
useful information as output.
Types of Computers W.R.T to Working and Structure:
There are different types of computer technology available these days. The functionality and data
processing of each type of computer is distinct and so are the output results.
Though, the methods/techniques, size, capacity, characteristics, and data handling aspects of each
computer may be different as well. Let us understand the different types of computers one by one
Types of Computers: Size
1. Micro Computers:
The microcomputer is also recognized as a personal computer, these are
comparatively economical. Microcomputers are small computers incorporating a
microprocessor, Central Processing Unit (CPU), memory, storage area, an input
unit, and an output unit.
It is a general-purpose computer that is outlined for personal use. Such computers
are made with minimum circuitry mounting over a single circuit board. They are fit
for personal work that may be making an assignment, at the office for office work,
watching a movie, etc. Examples include Desktop, Laptop, tablets, smartphones, etc.
2. The Mini Frame or Mini Computer:
Minicomputers are comparatively smaller than mainframe computers or can say a
minicomputer lies within the mainframe and microcomputer as it is smaller than
the mainframe but larger than a microcomputer.
Minicomputers are digital and multi-user computer systems with the connection of
more than one CPU. Thus, multiple users can work on these computers
simultaneously. Mini-frame computers are employed in institutes and
work units for tasks such as billing, accounting, and record management.
3. Mainframe Computer:
Computers utilized by large organizations to manage bulk data are designated as Mainframe computers.
Mainframe computers are multi-programming, high-performance and multi-user computers, which
implies they can manage the workload of more than 100 users at a time on the computer.
�2
The storage capability of the mainframe is enormous, with a high-speed
data process as well. The main purposes of such a type of computer
include managing customer statistics, census, and other heavy data in a
single device.
Mainframe computers, therefore, are mainly employed by departmental
and commercial organizations like Banks, Scientific research centers,
companies, and governmental departments like railways, paying
employees, ticket booking, maintaining details of purchases by users,
keeping detailed tax details, etc.
4. Supercomputer:
Supercomputers come under the biggest, fastest, powerful, and most expensive type of computer for
processing data type; they are designed to process an immense amount of data. A supercomputer can treat
trillions of instructions/directions in a second. It has thousands of interconnected processors.
Supercomputers are especially used in scientific and engineering
applications such as weather forecasting, quantum mechanics, climate
research, scientific simulations, nuclear energy research, etc. where a high
level of performance is required.
Examples: IBM Road burner, INTEL ASIC RED. PARAM-1000, BM Blue Gene,
and CRAY-XMP-14.
Types of Computers: Working Principle and Data
Handling Abilities
Analog Computer
Analog computers are outlined to process analog data. Analog data is continuous
data that varies continuously and cannot have discrete values. Analog computers are utilized primarily to
measure physical units like the voltage, electric current, pressure, temperature and convert them into
digits. Such computers are mostly used for scientific, technology, research, engineering, and industrial
applications.
Speedometer, mercury thermometer, thermometer, operational amplifiers, electric integrators, etc. are
examples of analog computers.
Digital Computer
The digital computer is outlined to execute calculations and logical operations at a high pace. Such
computers are proficient in solving problems in discrete formats. It acquires the raw data as input is in
the form of digits/binary numbers (i.e. 0 and 1) and processes it with programs stored in its memory to
produce the output.
�3
division, and all sorts of logical/mathematical operations as well. All modern computers like laptops,
desktops including smartphones, calculators, tablets, digital watches, accounting machines, workstations,
digital clocks etc. that we use at home or office are digital computers.
Hybrid Computer
Hybrid computers as the name signify exhibit features of both Analog and Digital computers. It is fast like
an analog computer and has memory and accuracy like those of digital computers. It can process both
continuous and discrete data. It takes analog signals and transforms them into digital form before
processing them.
These types of computers are extensively used in specialized applications where both analog and digital
data are processed. For example, a processor is applied in petrol pumps that converts fuel flow
measurements into quantity and price. Furthermore, they are used in airplanes, hospitals, and scientific
applications.