0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views8 pagesIssues Overview Report
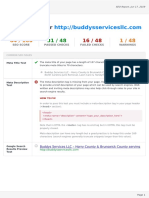
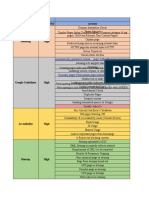
The document outlines various SEO issues and opportunities related to website optimization, including image alt text, URL structure, heading hierarchy, meta descriptions, and security warnings. It categorizes these issues by type and priority, providing recommendations for fixes to improve user experience and search engine visibility. Key areas of focus include ensuring proper use of headings, optimizing images, and addressing URL formatting to enhance site performance and usability.
Uploaded by
mslinhcontentCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as XLS, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views8 pagesIssues Overview Report
The document outlines various SEO issues and opportunities related to website optimization, including image alt text, URL structure, heading hierarchy, meta descriptions, and security warnings. It categorizes these issues by type and priority, providing recommendations for fixes to improve user experience and search engine visibility. Key areas of focus include ensuring proper use of headings, optimizing images, and addressing URL formatting to enhance site performance and usability.
Uploaded by
mslinhcontentCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as XLS, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 8