0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views3 pages???? ??????? ??????
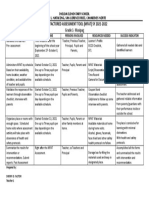
The document outlines essential considerations for designing an FTTH (Fibre to the Home) network, categorized into Initial Planning and Detailed Design Elements. Key factors include user density, environmental conditions, existing infrastructure, permitting, regulatory compliance, and future-proofing. The design must also address cost considerations, installation challenges, equipment selection, network scalability, security, and reliability to ensure a high-performance and sustainable network.
Uploaded by
Hsm AwanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views3 pages???? ??????? ??????
The document outlines essential considerations for designing an FTTH (Fibre to the Home) network, categorized into Initial Planning and Detailed Design Elements. Key factors include user density, environmental conditions, existing infrastructure, permitting, regulatory compliance, and future-proofing. The design must also address cost considerations, installation challenges, equipment selection, network scalability, security, and reliability to ensure a high-performance and sustainable network.
Uploaded by
Hsm AwanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3