0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views3 pagesBiology Class 10 - MCQ - 01 (Control and Coordination)
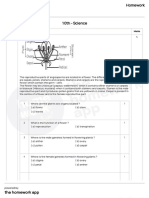
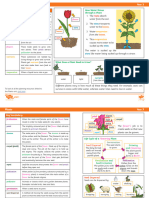
This document contains multiple choice questions for Class X students on the topic of Control and Coordination in plants and animals. It covers various concepts such as plant hormones, tropisms, and the nervous system. The questions are designed to test the understanding of key biological principles related to growth movements and physiological responses.
Uploaded by
Arpan SenCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views3 pagesBiology Class 10 - MCQ - 01 (Control and Coordination)
This document contains multiple choice questions for Class X students on the topic of Control and Coordination in plants and animals. It covers various concepts such as plant hormones, tropisms, and the nervous system. The questions are designed to test the understanding of key biological principles related to growth movements and physiological responses.
Uploaded by
Arpan SenCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3