0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views57 pagesLecture 5 - AI and ML
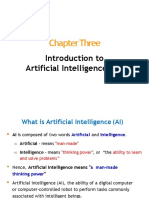
The lecture covers popular AI systems, definitions of AI, and its present and future implications. It discusses various AI applications, including search engines, voice assistants, and self-driving cars, while highlighting the differences between weak AI and strong AI. Ethical considerations and limitations of AI are also addressed, emphasizing the need for responsible development and governance.
Uploaded by
Mugdho SafayetCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views57 pagesLecture 5 - AI and ML
The lecture covers popular AI systems, definitions of AI, and its present and future implications. It discusses various AI applications, including search engines, voice assistants, and self-driving cars, while highlighting the differences between weak AI and strong AI. Ethical considerations and limitations of AI are also addressed, emphasizing the need for responsible development and governance.
Uploaded by
Mugdho SafayetCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 57