0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views4 pagesCloud Computing
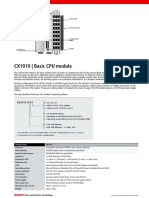
Cloud computing delivers computing services over the internet, allowing users to rent resources like storage and servers from providers such as AWS and Google Cloud. It offers key benefits including cost efficiency, scalability, and remote access, but also presents challenges like data security and internet dependency. Various service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) cater to different needs, and real-world applications span multiple industries, from healthcare to entertainment.
Uploaded by
haileymwenyeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views4 pagesCloud Computing
Cloud computing delivers computing services over the internet, allowing users to rent resources like storage and servers from providers such as AWS and Google Cloud. It offers key benefits including cost efficiency, scalability, and remote access, but also presents challenges like data security and internet dependency. Various service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) cater to different needs, and real-world applications span multiple industries, from healthcare to entertainment.
Uploaded by
haileymwenyeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4