0% found this document useful (0 votes)
278 views6 pagesO Level Computer Science (2210
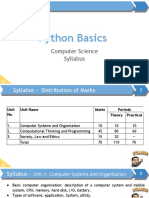
The Cambridge O Level Computer Science (2210) syllabus introduces students to computer science theory and practical skills, covering topics such as data representation, programming, and cybersecurity. The assessment consists of two papers focusing on theory and practical problem-solving using Python and SQL. Exam preparation tips include practicing past papers, mastering programming basics, and understanding key concepts in data representation and algorithms.
Uploaded by
mushtaqahmadkhannCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
278 views6 pagesO Level Computer Science (2210
The Cambridge O Level Computer Science (2210) syllabus introduces students to computer science theory and practical skills, covering topics such as data representation, programming, and cybersecurity. The assessment consists of two papers focusing on theory and practical problem-solving using Python and SQL. Exam preparation tips include practicing past papers, mastering programming basics, and understanding key concepts in data representation and algorithms.
Uploaded by
mushtaqahmadkhannCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6