0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesIntroduction To Database Security
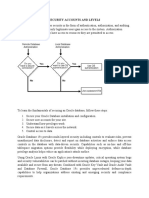
Database security in Oracle involves controlling user access and actions through schemas and security domains. Each user has a security domain that defines their privileges, roles, tablespace quotas, and resource limits. Oracle simplifies privilege management with roles, allowing users to manage related privileges collectively.
Uploaded by
vijaya2511Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesIntroduction To Database Security
Database security in Oracle involves controlling user access and actions through schemas and security domains. Each user has a security domain that defines their privileges, roles, tablespace quotas, and resource limits. Oracle simplifies privilege management with roles, allowing users to manage related privileges collectively.
Uploaded by
vijaya2511Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2