0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views21 pagesLinux Commands QA Part1
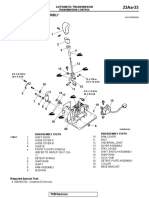
The document contains a comprehensive list of Linux commands along with questions and answers related to their usage. Each command is accompanied by a brief explanation of its function and syntax. The content is organized into multiple parts, covering a wide range of tasks from file manipulation to system monitoring.
Uploaded by
meme33823888Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views21 pagesLinux Commands QA Part1
The document contains a comprehensive list of Linux commands along with questions and answers related to their usage. Each command is accompanied by a brief explanation of its function and syntax. The content is organized into multiple parts, covering a wide range of tasks from file manipulation to system monitoring.
Uploaded by
meme33823888Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 21