100% found this document useful (1 vote)
402 views8 pagesTrunking Systems Notes
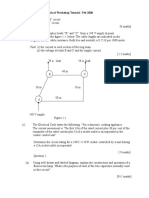
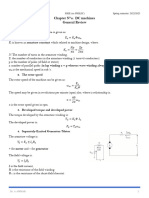
The document outlines safety measures, cable sizing, installation practices, and inspection procedures for electrical work, adhering to OSHA and IEC standards. Key safety protocols include the use of PPE, hazard identification, and proper work environments, while installation guidelines emphasize correct cable laying and accessory fixing. It also details testing methods such as visual inspections, continuity tests, and polarity tests to ensure safe and effective electrical installations.
Uploaded by
Kelvin MuriithiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
402 views8 pagesTrunking Systems Notes
The document outlines safety measures, cable sizing, installation practices, and inspection procedures for electrical work, adhering to OSHA and IEC standards. Key safety protocols include the use of PPE, hazard identification, and proper work environments, while installation guidelines emphasize correct cable laying and accessory fixing. It also details testing methods such as visual inspections, continuity tests, and polarity tests to ensure safe and effective electrical installations.
Uploaded by
Kelvin MuriithiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 8