CHAPTER CONTENT PAGE
NO. NO.
1. Introduction
Background of study
Significant of study
Statement of the problem
Objective of the study
Hypotheses
Operational defination
Assumptions
Delimitation
Conceptual framework
1
� CHAPTER – I
INTRODUCTION:
Technology came into the existence a very long time, but in the 21st century, it
started to expand rapidly. As a result the changes we can see in the world are still
the best changes so far. The transformation and development of technology that
not only improves our communication system but also makes our lifestyle a lot
easier than never anybody can dream of.
The unique invention of this technology is the mobile. We cannot think of living life
without mobile phones in the present day. In India, approximately every person
seems to have one. This mobile can be seen from a rickshaw puller to a high trader.
Nowadays mobile phone is not just used for communication, in addition, mobile
phones allow people to access different types of content, and for example, weather
update, news report, educational information, sports content, music videos and
much more.
Technological appliances are now very useful for higher education such as a laptop,
desktop, mobile, tablet, note etc. As we know that mobile is very much used by
students and they also used it for gathering information. Generally, it is easily
2
�accessible for everyone, because of the low price than other technological
equipment’s and it can be easily moved anywhere.
India is young. Nearly half of all Indians are under 30 years of age that is 550 million
youth which is equivalent of Western Europe and the USA Together. India appears
to be in the forefront of the developing market for Mobile phone (and data) services
to young people. India is the fastest Growing mobile subscribed base in the world
with 950 million users. 81% of India uses a mobile phone, 10% of India uses a smart
phone Where as 9% of India use a multimedia phone. Surveys and studies from A
number of countries indicate that the use of mobile phones in young People is
increasing rapidly and starting at a younger age.
Almost half of The mobile internet users are between 18 and 25 years. Studies show
Varying prevalence of use at different ages in different countries. According to the
Wireless World Forum, a research consultancy, the Number of young people using
mobile voice and data services in the Asia Pacific region will be more than double
from 71-million in 2004 to 151- Million in 2007. India’s mobile youth market will
grow 300 present from 2005 through 2007, from 8.3-million to 27.6-million people.
This means India will account for 18.3 percent of this large and growing market.
India’s young people spent US $437-million on mobile telephone Services in 2004
and US $856-million in 2005.
3
�And by 2007 this Expenditure was almost triple to $ 2.5-billion. In India every
household item is social. The Mobile is the only item Which qualifies to become the
first personal, protected and private itemof possession. It gives a great high to
anyone to own such personal and private item. Ease to early adoption is another
significant affordability and coverage of mobile telephony services and its
increasing importance as a means of two way communication are responsible for
the rapid expansion of mobile telephony all over the world. Studies have proven
that rampant use of social networking, texting and chatting on mobile phones result
in lower grades and poor academic performance of students.
While people of various ages find mobile phones convenient and useful, younger
generations tend to appreciate them more and be more dependent on them. The
researches have proven that some students have the habit of keeping their mobile
phones on during classes and studies, even in the library, thereby distracting others.
In this context the study focused on finding the influence of mobile phone use on
academic performance of students
In the chronological analysis of mobile phones made by Ling (2002), it is stated that
in the year 1997 its use
Was oriented mainly to work matters and more men than women where in
possession of a mobile phone. In 1999 there were no differences by gender because
both used them; however, there was a debate aboutWhether the use of mobile
phones posed a risk if used while driving or because it emitted electromagnetic
Radiations, so there were people who chose not to have one.
4
�BACKGROUND OF THE STUDY:
A background for a study on mobile phone addiction among school students
should acknowledge the prevalence and potential negative impacts of excessive
mobile phone use, highlighting the need for research in this area. It should also
consider factors that contribute to addiction, such as socioeconomic status, family
structure, and academic performance. Additionally, the background should address
the potential consequences of mobile phone addiction on students' academic
performance, mental health, and social interactions.
Here's a more detailed breakdown:
1. 1. Prevalence and Concern:
Mobile phone addiction is increasingly recognized as a significant public health
concern, particularly among adolescents. Research indicates that a substantial
percentage of school students are experiencing excessive mobile phone use,
leading to potential negative consequences.
2. 2. Potential Negative Impacts:
Excessive mobile phone use can negatively impact various aspects of
students' lives:
5
� o Academic Performance: Distractions, reduced focus, and time spent on
non-academic activities can lead to lower grades and poor academic
outcomes.
o Mental Health: Studies suggest a link between mobile phone addiction
and depression, anxiety, and loneliness.
o Social Interactions: Excessive phone use can lead to reduced face-to-
face interactions and a weakening of social skills.
3. 3. Contributing Factors:
Several factors can contribute to mobile phone addiction in school students:
o Socioeconomic Status: Research suggests a correlation between higher
socioeconomic status and mobile phone addiction, possibly due to
greater access to devices and the potential for exposure to addictive
online content.
o Family Structure: Nuclear families and families with multiple siblings
may be associated with higher rates of mobile phone addiction.
o Academic Performance: Studies have shown that students with lower
academic performance may be more prone to mobile phone addiction as
a coping mechanism or a way to escape from academic pressures.
6
�SIGNIFICANT/ NEED OF STUDY:
A study on mobile phone addiction among school students is
crucial for several reasons:
➢ Understanding the Problem:
It can help researchers gain a deeper understanding of the extent and nature
of the problem.
➢ Identifying Risk Factors:
It can help identify the factors that contribute to mobile phone addiction,
allowing for targeted interventions.
➢ Developing Solutions:
The findings can inform the development of effective strategies to address
mobile phone addiction and its negative consequences.
➢ Addressing gaps in knowledge:
A study might be needed because existing research doesn't fully explore a
topic, leaves unanswered questions, or lacks a certain perspective.
➢ Responding to a real-world problem:
7
� Research might be crucial for understanding and addressing pressing issues
like climate change, poverty, or public health crises.
➢ Contributing to a field's advancement:
Studies can be vital for pushing the boundaries of a discipline, developing
new theories, or refining existing methodologies.
➢ Reflecting societal needs:
Research may be necessary to inform public policy, improve educational
practices, or enhance societal well-being.
➢ Building upon previous work:
Studies can build upon existing findings, refine methodologies, or test the
validity of previous research.
In essence, a "significant need for study" emphasizes the relevance and
importance of a research project, making it worthwhile and likely to have a
meaningful impact
STATEMENT OF PROBLEM:
A descriptive study to assess the knowledge regarding mobile addiction
among the schooling children at william hospital in kanyakumari district
8
�OBJECTIVE OF STUDY:
The following are the objectives of the study undertaken by the
investigator:-
➢ To find the difference in smart phone addiction among higher secondary
school students with respect to their gender i.e. boys and girls.
➢ To find the difference in smart phone addiction among higher secondary
school students with respect to their type of institutions i.e. govt. and private.
➢ To find the difference in the smart phone addiction of higher secondary
school students in interactional effect of gender (boy and girl) and type of
institutions (govt. and private) when smart phone addiction scores are taken
as dependent variable.
HYPOTHESES OF THE PRESENT STUDY
Keeping in view the aims of the present study, following
Hypotheses were formulated : -
➢ There is no significant difference in smart phone addiction among Higher
secondary school students with respect to their gender i.e. Boys and girls.
9
� ➢ There is no significant difference in smart phone addiction among Higher
secondary school students with respect to their type of Institutions i.e. govt.
and private.
➢ There is no significant difference in the smart phone addiction of Higher
secondary school students in interactional effect of gender (boy and girl) and
type of institutions (govt. and private) when Smart phone addiction scores
are taken as dependent variable.
OPERATIONAL DEFINATION:
An operational definition for mobile phone addiction among school students could
be: “The excessive and persistent use of a mobile phone, despite negative
consequences in academic performance, social interactions, and overall well-being,
characterized by a lack of control, withdrawal symptoms when deprived of phone
use, and a focus on the phone at the expense of other activities.” This definition
focuses on behaviors and their measurable impact, making it practical for research
and assessment.
Here's a more detailed breakdown of the key components of this definition:
10
�➢ Excessive and persistent use:
This refers to the amount of time spent on the phone daily, weekly, or over a
specific period, as well as the frequency of use throughout the day.
➢ Negative consequences:
This includes low grades, difficulty concentrating in class, reduced social
engagement with peers or family, and potential mental health impacts like
anxiety or depression.
➢ Lack of control:
This involves the inability to regulate the amount of time spent on the phone
or the specific apps used, even when experiencing negative consequences.
➢ Withdrawal symptoms:
These can include restlessness, irritability, or a sense of discomfort when the
phone is unavailable or use is restricted.
➢ Focus on the phone:
This refers to the preference for phone use over other activities, even when
those activities are more beneficial or enjoyable.
This operational definition allows researchers and educators to identify and
measure mobile phone addiction in school students, enabling the
development of intervention and prevention strategies. It focuses on
observable behaviors and quantifiable results, making it a practical and
useful tool for research and practice.
11
�ASSUMPTIONS:
Assumptions about mobile phone addiction among students often focus on the
phone itself being the addictive substance, but research suggests that addiction is
more likely a behavioral or psychological issue, not just a device-related one.
Common assumptions include students being easily distracted by their phones,
using them to escape social situations or problems, and being more prone to
addiction due to their age and lack of self-control.
Here's a more detailed breakdown of common assumptions and the research that
challenges them:
Common Assumptions:
Phones are inherently addictive:
This is a broad assumption that doesn’t account for the various reasons why
someone might become attached to their phone.
Students are more susceptible:
While students are a significant group affected by phone addiction, this assumption
doesn’t consider individual differences in personality, coping mechanisms, and
underlying mental health issues.
Phones are primarily used for entertainment:
This overlooks the fact that phones are also used for communication, academic
purposes, and other functional tasks.
Phone addiction is solely a social media issue:
12
�While social media can contribute to addiction, the use of other apps, games, and
features on phones also play a role.
Addiction is solely a physical issue:
This neglects the psychological aspects of addiction, such as anxiety, depression,
and the need to avoid negative emotions.
Challenges to these Assumptions:
Phone use is often a coping mechanism:
Students may use their phones to deal with stress, anxiety, or low self-esteem,
making it a way to manage their emotions rather than a direct source of addiction.
Addiction is a complex issue:
It’s not solely about the phone itself, but also about individual vulnerabilities, social
pressures, and the specific behaviors and apps used on the phone.
Habitual use vs. Addiction:
Research suggests that phone use is more often a habit than a true addiction, and
that framing it as a habit can be more helpful for understanding the behavior.
The role of other factors:
Factors like childhood trauma, loneliness, and lack of self-control can significantly
contribute to phone addiction.
13
�DELIMITATION
A delimitation for studying mobile phone addiction among school students
would involve setting clear boundaries for the research, focusing on specific
aspects of the phenomenon. This could include defining the age range of
students, the types of schools (public vs. private, etc.), the scope of addiction
(e.g., specific apps used or behaviors), and the geographical location of the
study.
Here's a more detailed breakdown of how you can define a delimitation:
1. Student Population:
• Age Range:
Specify the grade levels or ages of students included in the study (e.g., middle
school, high school, specific grade levels).
• School Type:
Indicate whether the study focuses on public schools, private schools, or a mix.
• Geographical Location:
Define the region, city, or specific school(s) where the research is conducted.
2. Addiction Scope:
• Types of Mobile Phone Use:
14
� Specify the focus (e.g., social media use, gaming, excessive texting, calling,
etc.).
• Specific Apps/Services:
Indicate if the study will examine addiction related to particular apps or online
platforms.
• Severity of Addiction:
Define the criteria for measuring addiction, including frequency of use, time
spent, impact on daily life, and potential withdrawal symptoms.
3. Research Focus:
• Impact on Academic Performance:
Delimit the study to investigate the relationship between mobile phone
addiction and academic outcomes, such as grades, attendance, or test scores.
• Impact on Mental Health:
Focus on the effects of addiction on students' mental well-being, such as stress,
anxiety, depression, or social isolation.
• Impact on Social Life:
Examine how addiction affects students' social interactions, relationships with
peers, and family communication.
15
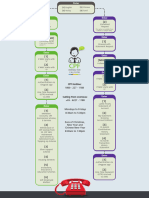
�CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
A conceptual framework for mobile phone addiction among students recognizes it
as a form of behavioral addiction, often characterized by an excessive and
compulsive use of smartphones, leading to negative consequences for social,
psychological, and academic well-being. It also highlights the influence of various
factors like parental control, social interactions, personality traits, and the perceived
environment on the development and maintenance of this addiction.
16
�17