0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views16 pagesComputer Note
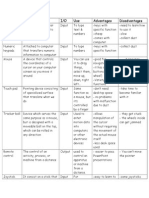
Input devices are hardware that send data to a computer, enabling user interaction and control. Common types include keyboards, mice, scanners, microphones, and biometric devices, each with specific uses, advantages, and disadvantages. Keyboards and mice are essential for navigation and data entry, while scanners and microphones facilitate document digitization and audio capture.
Uploaded by
kevinnkwedeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views16 pagesComputer Note
Input devices are hardware that send data to a computer, enabling user interaction and control. Common types include keyboards, mice, scanners, microphones, and biometric devices, each with specific uses, advantages, and disadvantages. Keyboards and mice are essential for navigation and data entry, while scanners and microphones facilitate document digitization and audio capture.
Uploaded by
kevinnkwedeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 16