0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views16 pagesProcessors
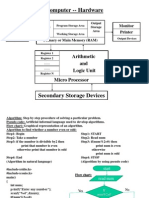
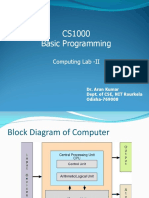
The document provides an overview of various language processors, including interpreters, compilers, and just-in-time compilers, detailing their functions and outputs. It includes comparisons of language speeds and examples of compiling a simple program, demonstrating the steps from source code to machine code. Additionally, it illustrates the processes of lexical analysis, parsing, semantic analysis, and code generation.
Uploaded by
gogimo1970Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views16 pagesProcessors
The document provides an overview of various language processors, including interpreters, compilers, and just-in-time compilers, detailing their functions and outputs. It includes comparisons of language speeds and examples of compiling a simple program, demonstrating the steps from source code to machine code. Additionally, it illustrates the processes of lexical analysis, parsing, semantic analysis, and code generation.
Uploaded by
gogimo1970Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 16