0% found this document useful (0 votes)
186 views10 pagesWeb Technology II
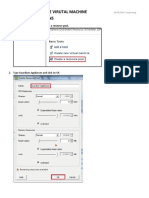
Web technology encompasses tools, languages, and techniques for building and managing websites and applications, including both front-end and back-end components. The World Wide Web (WWW) is a system of interlinked documents accessed via web browsers, and protocols like HTTP and FTP govern data transmission. JavaScript is a key programming language for creating interactive web pages, with client-side and server-side scripting capabilities, and can be integrated into HTML through inline, internal, or external methods.
Uploaded by
nurmohammad0560Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
186 views10 pagesWeb Technology II
Web technology encompasses tools, languages, and techniques for building and managing websites and applications, including both front-end and back-end components. The World Wide Web (WWW) is a system of interlinked documents accessed via web browsers, and protocols like HTTP and FTP govern data transmission. JavaScript is a key programming language for creating interactive web pages, with client-side and server-side scripting capabilities, and can be integrated into HTML through inline, internal, or external methods.
Uploaded by
nurmohammad0560Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10