0% found this document useful (0 votes)
90 views20 pages8.microservices Notes
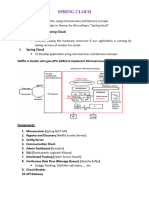
The document provides a comprehensive overview of microservices architecture, detailing its advantages over monolithic architecture, including reduced server burden and improved maintenance. It outlines various components of microservices such as service registry, API gateway, and circuit breaker, along with their functionalities and implementation steps. Additionally, it discusses challenges faced in microservices, such as bounded context and repeated configurations, and emphasizes the importance of tools like Spring Boot, Docker, and Kubernetes in developing microservices applications.
Uploaded by
Saim KeshriCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
90 views20 pages8.microservices Notes
The document provides a comprehensive overview of microservices architecture, detailing its advantages over monolithic architecture, including reduced server burden and improved maintenance. It outlines various components of microservices such as service registry, API gateway, and circuit breaker, along with their functionalities and implementation steps. Additionally, it discusses challenges faced in microservices, such as bounded context and repeated configurations, and emphasizes the importance of tools like Spring Boot, Docker, and Kubernetes in developing microservices applications.
Uploaded by
Saim KeshriCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 20