0% found this document useful (0 votes)
359 views13 pagesUnit 1 Computer Systems and Organisation
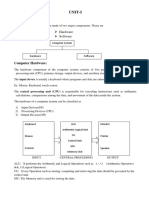
This document provides an overview of computer systems and organization, detailing the components of a computer system including input and output devices, CPU, memory types, and storage devices. It also covers software types, including system software and application software, and explains the role of operating systems in managing hardware and resources. Additionally, it discusses programming languages and tools used for software development.
Uploaded by
manishadthakur18Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
359 views13 pagesUnit 1 Computer Systems and Organisation
This document provides an overview of computer systems and organization, detailing the components of a computer system including input and output devices, CPU, memory types, and storage devices. It also covers software types, including system software and application software, and explains the role of operating systems in managing hardware and resources. Additionally, it discusses programming languages and tools used for software development.
Uploaded by
manishadthakur18Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 13