JKSSB – Computer Knowledge
Lecture 6-Part2
Network Models
For more study material form Nitesh For doubt discussions and Preparation
Sir follow the telegram channel strategy. Or guide you in right
t.me/jkutjobs direction. Like and msg me on my
Facebook page.
www.facebook.com/niteshsharmajk
telegram
�How data is shared between two computers
over a network?
• Computers has NIC(network interface cards)
• Connected with Lan cable connected with each other can share data
with each other.
• But if one has Window and one has MAC OS then
how?
• There are models for that
1. OSI Model
2. TCP/IP Model
� • Developed by ISO
Open system interconnection model (OSI Model) • Has 7 layers
• Is Intangible
Application layer Application Layer
Used by network applications (computer applications that use internet)
Example google chrome (uses Application layer protocol, to do Web surfing), skype
Presentation Layer For FILE TRANSFER – with the help of FTP protocol
For WEB SERFING - with the help of HTTP/HTTPs protocol
For Emails - SMTP protocol is used
Session Layer Virtual Terminals – Telnet is used
Presentation layer
Transport Layer - Data form application layer is taken to Presentation layer in form of Characters and
Numbers(ASCII).
SEGMENT - It Translates these into the Machine understandable Binary format
Example from ASCII to EBCDIC
Network Layer - Before data is transfer further to session layer, it performs the bit reduction, called
PACKETS DATA COMMPRESSION (it can be lossy or lossless)
- Data compression reduces the amount of space used to store the original file. (it
Data Link Layer can be received at the destination in a very less time, thus faster data transmission
FRAME Example: - real time video and audio streaming)
- Before the data is transferred further data is encrypted (at sender side ) and is
Physical layer Decrypted (at receiver side) using SSL protocol ( secure sockets layer)
1st layer
�Session layer
As you need helpers in a party, for staring and closing the party.
• Similarly, It helps in setting up and managing connections and mainly sending and receiving the data, followed by terminations of connections and
sessions.
• Its helpers are: -
APIs - (application programming interfaces )
e.g., NETBIOS – (network basic input output system)
- this allows applications on different computers to communicates with each other.
• Just a commuter is connect to a server, it performs a function Authentication (who you are?) – if accepted a session setup for you.
• Then server performs Authorization (will check if you haver permission to access this file) if yes you will access the data in the form of data packets.
• Session layer keep tracks which data packet belongs to which data types (like image or text). Hence Session Management
Transport layer
Break data into Segments (Segmentation) – data divided into small data unit.
Flow Control – control the amount of data being transmitted. (our speed of getting data should be same as that of server sending data and vice versa)
Error Control – if there is some loss of data, it creates a automatic repair request to send the missing data again.
Has two protocols
1. TCP(Transmission control Protocol) – for connection oriented transmission(better because data is always delivered| so used where full data delivery is
must like in E mail, www, FTP)
2. UDP (User datagram protocol ) – for connectionless transmission (faster than TCP because it does not provide any feedback if data was actually
delivered| used in videos, games, calling)
Network Layer
• Works for the transmission of the received data segments form one computer to another located in different network.
• In this layer Routers resides - Logical addressing (IP addressing for each data packet to reach the correct destination), Routing(process to take the data
packet to the destination), Path Determination (to find the best possible path to data delivery form source to receiver using – OSPF, BGP, IS- IS protocol)
�Data Link Layer
• Receive data packet form the network layer | Data packet contains the IP address of sender and receiver
• Two kind of addressing -
Logical Addressing at Network layer - sender and receiver IP address were assigned to each
assignment to form a data packet.
Physical Addressing at Data link layer – MAC address of sender and receiver are assigned to the data
packet and forms a frame.
{ MAC address is a 12 digit alpha numeric number embedded in NIC of your computer.}
It also provides means to transfer data via a local media (electronic signal – copper wire | light signal – optical wire |
radio wave – air)
So finally two basic functions of Data Link Layer are:
1. Accessing the Media – by Framing
2. Controls how data is placed and received from the media – using techniques “Media Access Control” and “error
detections”
3. CSMA (carrier sense multiple access) – to handle more data packets to send over a same media with out any
collisions.
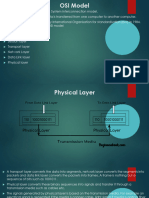
Physical Layer
• Frames are now converted form Binary signals into electrical or light or radio wave signals depending on the type of
media.
• Finally it reaches the receiver and via application layer it reaches the receiver computer.
�TCP/IP Model
• It is a tangible, Client – Server model
• 4 layers
It contains high level protocols, TELNET, FTP, SMTP, DNS, HTTP, NNTP,
Application layer DHCP, are used.
• It is like a transport layer in the OSI model.
• Two end to end transport protocols are used.
Transport Layer • Transmission control protocol (TCP) and use datagram protocol (UDP)
• Transfers the IP packets (IP Datagrams) to the destination.
Internet Layer • IP, ICMP, ARP, RARP and IGMP have used protocols
Host to Host • The host has connected to the network using the protocol to
send IP packets.
• Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI, Frame relay are used here.
Network Layer
� Thankyou
Please Share!!!