0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views4 pagesData Abstraction in DBMS
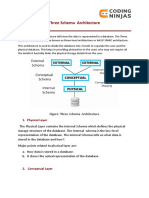
Data abstraction in DBMS is the process of hiding irrelevant details from users, allowing them to access only necessary information while keeping data secure. There are three levels of data abstraction: physical (how data is stored), logical (what data is present and its relationships), and view (user-specific data representation). Data independence allows changes at one schema level without affecting others, with two types being logical and physical data independence.
Uploaded by
yharshyadavh20Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views4 pagesData Abstraction in DBMS
Data abstraction in DBMS is the process of hiding irrelevant details from users, allowing them to access only necessary information while keeping data secure. There are three levels of data abstraction: physical (how data is stored), logical (what data is present and its relationships), and view (user-specific data representation). Data independence allows changes at one schema level without affecting others, with two types being logical and physical data independence.
Uploaded by
yharshyadavh20Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4