0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views33 pagesCSS With Box, Column, Table and List
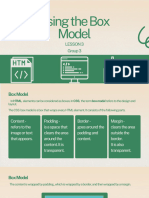
Module 4 covers various CSS concepts including applying CSS to text, the box model, and layout techniques. It explains the use of web fonts, text styling, and the structure of the box model with its components such as content, padding, border, and margin. Additionally, it discusses properties for managing dimensions, borders, and shadows in CSS.
Uploaded by
lavanyalavanya9388Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views33 pagesCSS With Box, Column, Table and List
Module 4 covers various CSS concepts including applying CSS to text, the box model, and layout techniques. It explains the use of web fonts, text styling, and the structure of the box model with its components such as content, padding, border, and margin. Additionally, it discusses properties for managing dimensions, borders, and shadows in CSS.
Uploaded by
lavanyalavanya9388Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 33