0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views28 pagesOSI Reference Model
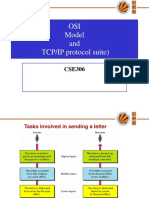
The OSI model, established by the International Standards Organization, is a framework for understanding network communications, consisting of seven layers. These layers are categorized into network support layers (Physical, Data Link, Network), transport layer, and user support layers (Session, Presentation, Application), each with specific responsibilities. The model facilitates interoperability among different software systems and ensures reliable data transmission across networks.
Uploaded by
dpdhore95Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views28 pagesOSI Reference Model
The OSI model, established by the International Standards Organization, is a framework for understanding network communications, consisting of seven layers. These layers are categorized into network support layers (Physical, Data Link, Network), transport layer, and user support layers (Session, Presentation, Application), each with specific responsibilities. The model facilitates interoperability among different software systems and ensures reliable data transmission across networks.
Uploaded by
dpdhore95Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 28