0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views10 pagesDefect Management
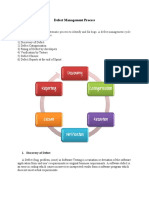
The document outlines the defect management process in software testing, defining bugs and defects, and detailing the components of a bug report. It describes the stages of defect management, including discovery, categorization, resolution, verification, and reporting, emphasizing the importance of tracking and fixing defects effectively. Additionally, it introduces key defect metrics such as defect rejection ratio (DRR) and defect leakage ratio (DLR) to evaluate the quality of test execution.
Uploaded by
Atharva KulkarniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views10 pagesDefect Management
The document outlines the defect management process in software testing, defining bugs and defects, and detailing the components of a bug report. It describes the stages of defect management, including discovery, categorization, resolution, verification, and reporting, emphasizing the importance of tracking and fixing defects effectively. Additionally, it introduces key defect metrics such as defect rejection ratio (DRR) and defect leakage ratio (DLR) to evaluate the quality of test execution.
Uploaded by
Atharva KulkarniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10