Website: https://duranta.
app/
COMPUTER SCIENCE (POST RELATED) Subject
Code: 971 (324-CSE, CS-114, C-304)
Programming: Introduction to computer programming. Assembling language programming.
Problem solving techniques, algorithm specification and development. Programming style,
testing and debugging. Program design techniques: Structured and modular program design.
Programming languages and paradigms: classification. Programming in C: Data type, statements,
control structures, arrays, pointers, strings, functions, preprocessor directives, structures, unions
and bit-fields, files. Introduction to object-oriented programming: Encapsulation, inheritance and
polymorphism, Mechanic Language Programming, Template functions and classes multi-threads
exceptions, Class and object. Introductory programming with C++/JAVA.
Digital System: Number system: binary, octal, hexadecimal and BCD. Data representation.
Logic gates and Boolean algebra: Combinational circuits. Circuit design using logic gates.
Circuit and expression minimization: Karnaugh map and Quine-McCluskey. Basic flip-flops
(FF), Design of half and full adder. Basic counters and register. Basic decoders, encoders,
multiplexers and demultiplexers. ADC and DAC circuits. PLA design, Pulse mode and
fundamental mode logic, Pulse & switching units, Newtrivibrations, Digital LC: DTL, TTL, III,
CMOS MOS gates, Memory system, LED, LCD applications of Op-Amps. Comparators.
Discrete Mathematics: Prepositional and predicate calculus: Basic concept. Theory of sets: set
operations, algebra of sets. Mathematical induction. Basic concept of relations and its
representation. Functions and its classification and pictorial representation. Graph theory and its
application. Elementary number system. Principles of counting. Reversion, generating, functions,
recurrence relation.
Numerical Analysis: Solving linear systems with Gaussian elimination and Gauss-Jordan
elimination method. Interpolation: Newton’s formula, LaGrange’s formula. Numerical
differentiations and integrations: Trapezoidal, Simpson’s 1/3rd and 3/8th rule. Romberg
integration. Solutions and Newton-Raphson’s method. Solution of ordering differential equation
and least square approximation of functions.
Data Structures: Arrays: Representation and operations. Sparse and dense matrices: Concept
and operation. Stacks and queues: Concept, structures and basic operations. Quick-sort and
Polish notation: Applications of stack. Recursion: Concept and applications. Linked lists:
Representation and various operations. Trees: Binary trees, traversing binary trees. Binary search
trees: Various operations. Binary heaps: Heap sort. Huffman’s algorithm. Graphs:
Representations and operations. Spanning trees, shortest path and topological sorting. Internal
sorting: Insertion sort, selection sort, merge-sort, radix sort, Basic hashing techniques.
https://www.facebook.com/groups/govtcse.itjob/ https://www.facebook.com/duranta.ac
� Website: https://duranta.app/
Microprocessor and Interfacing: Microprocessor and microcomputers. Evolution of
microprocessor. Architecture of a general-purpose microprocessor and its operation. Addressing
modes. Common instruction types: Basic assembly instruction set. Intel 8086 microprocessor:
Internal architecture, register structure, programming model, addressing modes and instruction
sets. Interrupts its classification and interrupt handling, Memory management in Intel 80x86
family: Real-mode memory management, segmentation and segmented to physical address
translation. Protected mode memory management: Segmentation and virtual addressing, segment
selectors and descriptors and tables. Intel 80386 and 80486 register formats. Paged memory
operation and TLB structure I/O port organization and accessing. Interfacing the keyboard,
printer and monitor. Structure and operation of certain chips as 8255A, 8253, 8272, 8259A,
8237. Bus interfaces and micro controllers.
Computer Organization and Architecture: Fundamentals of computer design. Processor and
ALU design. Control design: Hardware control and micro-programmed control. Caches Memory
organization. Exceptions System organization Bus and hazards I/O subsystem and I/O processor.
Parallel processing: Concept, pipeline processors. Interrupts systolic arrays and fault-tolerant
computers.
Compiler Design and theory of computation: Introduction to compiler. Basic issues, lexical
analysis, logical analysis, syntax analyses. Semantic analysis, type checking, run-time
environments, code generation, code optimization and language theory.
Algorithm:
Algorithm and complexity: Asymptotic notations, Basic algorithm techniques and analysis,
Divide and conquer, Dynamic programming, greedy method, branch and bound, string matching,
computational geometric problems, graph algorithms, spanning. trees, shortest paths, max-flow
problem, searching algorithms. Techniques for analysis of algorithms, approximation algorithms,
parallel algorithms.
Operating System: Introduction, evolution, goals and components of OS. Types of OS Process
management: Process states PCB, job and process scheduling. CPU scheduling algorithms,
critical section problems and solutions. Semaphores, Inter-process communication techniques.
Deadlock handling methods. deadlock, banker’s algorithm. Memory management techniques:
Paging, segmentation and page replacement policies. (FIFO, LIFO, LRU) Secondary storage
management, Disk scheduling algorithms. Kernel, Shell File management: File system structure,
organization, FCB, space allocation, tree structured file system. Protection and security:
classification and handling techniques.
https://www.facebook.com/groups/govtcse.itjob/ https://www.facebook.com/duranta.ac
� Website: https://duranta.app/
Database Management System: Definition of DBMS, types of DBMS, its advantages and
disadvantages, Data model: ER model and relational model. Integrity constraints. Functional
dependencies. Assertions and triggers. File organization: Definition of various file organization,
classification and Representation. Indexing techniques: sparse and dense indexing. B+ tree
indexing, hash indexing. Relational database design: normalization, 2NF, 3NF and BCNF. Query
processing: Various notations, cost estimation of selection operation and join operation.
Transaction concept and concurrency control: Lock based protocol, deadlock handling. SQL and
application using SQL.
Software Engineering
Introduction, Software process. Project management. Requirements engineering processes.
System Models: Context, data, behavioral and object models: agile, waterfall model ,prototype,
SCRUM,Spiral;Object oriented design techniques: Model , UML use case, class, Real-time
software design. System design with reuse. Critical system design dependability, software
maintenance, critical system specification and development Verification and validation. Software
testing. Software cost estimation: COCOMO model Halstead formula, Graph: Cel analysis of
complexity measures, software reliability and availability, Quality assurance.
Data Communication: Introduction to OSI and TCP/IP protocol. Data transmission basics:
analog and digital data, spectrum and bandwidth. Transmission impairments. Data rate channel
capacity. Transmission media: Twisted pair, coaxial cable and optical fiber, wireless
transmission. Data encoding: NRZ. NRZI, Manchester and differential Manchester modulation
techniques-AM, FM, PM, Della modulation, compounding Equations, ASK, PSK, FSK. QPSK.
QAM sampling theorem, PCM. PPM. PAM. Data transmission: Synchronous and asynchronous
and asynchronous. NULL modem configuration. Data link control error and flow control CRC
and HDLC. Multiplexing: FDM, TDM, statistical TDM. Basic circuit switching and packet
switching techniques.
Computer Network and Internet: Protocol, fundamentals of control protocol, Introduction and
network types, LAN, MAN, WAN. Topologies: Star, switched, bus, ring. Ethernet LAN
standards. Internetworking: Network interconnection, bridges, routers. Network layer protocols:
IP, ARJP, ICMP, IP addresses. Unicast and multicast routing protocols. IPV6 congestion control,
Transport layer protocol: TCP and UDP. Introduction to wireless LAN, VSAT, analog and
digital cellular system. Network security: Types of attack, encryption techniques and digital
signatures, Cryptography= encryption, decryption, ATM protocol; DNS, HTTP, Email.
Artificial Intelligence:
Overview of AI. General concepts of knowledge. Introduction to PROLOG. Knowledge
representation. Intelligent agents. First order logic. Knowledge organization and manipulation:
https://www.facebook.com/groups/govtcse.itjob/ https://www.facebook.com/duranta.ac
� Website: https://duranta.app/
Search strategies, matching techniques and game planning. Natural language processing,
Probabilities reasoning, expert systems and computer vision, Knowledge acquisition: Learning in
symbolic and non-symbolic representation.
INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY
(POST RELATED)
Subject Code: 281
(ICT-132, SE-332, ECE-349, ETE-351, CS&TE-363, IT-364, AP&ETE 365, AP&TE-366)
Basic Physics
Basic elements: charge, Coulomb ‘s law, electric field, Gauss ‘s law, electric potential, magnetic
field; Faraday ‘s law, Maxwell ‘s equations, Waves and oscillations, Theory of special relativity,
Electromagnetic waves, Photoelectric effect, Quantum theory of light, X-ray and X-ray
diffraction, Compton effect; De Broglie waves, Phase and group velocity, Wave function and
wave equation.
Introduction to Computer Systems
Introduction to computations; Early history of computing devices; Computers; Major
components of a computer; Hardware: processor, memory, I/O devices; Software: Operating
system, application software; Basic architecture of a computer; Basic Information Technology;
The Internet; Number system: binary, octal, hexadecimal, binary arithmetic.
Electrical Circuits
Circuit variables and elements: voltage, current, power, energy, independent and dependent
sources, resistance; Basic laws of electrical circuits: Ohm‘s law, Kirchhoff’s current law (KCL)
and Kirchhoff’s voltage law (KVL); Simple resistive circuits: series and parallel circuits, voltage
and current division, source transformation; Methods of analysis: nodal and mesh analysis;
Circuit theorems: Thevenin‘s, Norton‘s and superposition theorems, maximum power transfer
and reciprocity theorem; Capacitors and inductors: inductors and capacitors, their characteristics,
series-parallel combination of inductors and capacitors; RLC Transients. Series and parallel AC
circuits: impedance and phasor diagram, series and parallel networks, voltage divider rule,
admittance and susceptance; mesh and nodal analysis, wye-delta and delta-wye conversions;
superposition theorem, Thevenin ‘s theorem, Norton ‘s theorem, maximum power transfer
theorem.
Digital Logic Design
Digital logic: Boolean algebra, De Morgan's Theorems, logic gates and their truth tables,
canonical forms, combinational logic circuits, minimization techniques; Arithmetic and data
handling logic circuits, decoders and encoders, multiplexers and demultiplexers; Combinational
circuit design; Flip-flops, race around problems; Counters: asynchronous counters, synchronous
https://www.facebook.com/groups/govtcse.itjob/ https://www.facebook.com/duranta.ac
� Website: https://duranta.app/
counters and their applications; PLA design; Synchronous and asynchronous logic design; State
diagram, Mealy and Moore machines; State minimizations and assignments; Pulse mode logic;
Fundamental mode design.
Basic Electronics
Diode circuit: current-voltage characteristics of a diode, DC and AC models, dynamic resistance
and capacitance, load line, Zener regulator, half wave and full wave rectifier, voltage multiplier,
clipper and clamper; Bipolar junction transistors: construction and operation, amplifying action,
common base, common emitter, common collector, load line, different biasing, stability factor,
small signal equivalent circuit models, BJT as a switch; Single stage amplifier: voltage and
current gain, input and output impedance of a common base, common emitter and common
collector, h-parameter; Field effect transistor (FET): JFET structure, operation and
characteristics. MOSFET construction, operation and characteristics.
Microprocessor and Interfacing
Introduction to microprocessor: overview of computer architecture, evolution of
microprocessors, difference between microprocessor and microcontroller; Introduction to
8086/8088: basic architecture of 8086, memory segmentation, flags, addressing modes, pins &
signals, single and multi-processor systems; Microprocessor programming: instruction sets,
introduction to assembly language programming; Tools: assemblers, debuggers, development
systems; Clock and bus controller interfacing: clock generator, bus demultiplexer, bus controller
interfacing; Memory Interfacing: SRAM and EEPROM interfacing, Types of I/O: parallel I/O,
programmed I/O, interrupt driven I/O, I/O port address decoding, programmable peripheral
interface (8255A), interface examples– Keyboard matrix, LCD/7-Segment display, printer,
stepper motor, A/D and D/A converter; Timer interfacing: The 8254 programmable interval
timer (PIT), timing applications; Serial I/O interface: asynchronous and synchronous
communication, physical communication standard-EIA RS232, programmable communication
interface, interfacing serial I/O devices- mouse, modem, PC Keyboard; Interrupts: interrupt
driven I/O, software & hardware interrupts, interrupt vectors and vector table, interrupt
processing, programmable interrupt controller (8259A), DMA: DMA controller (8237).
Computer Architecture
Information representation; Measuring performance; Instructions and data access methods:
operations and operands of computer hardware, representing instruction, addressing styles;
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) operations, floating point operations, designing ALU; Processor
design: data paths & single cycle and multicycle implementations; Control Unit design -
hardwired and microprogrammed; Hazards; Exceptions; Pipeline: pipelined Datapath and
control, superscalar and dynamic pipelining; Memory organization: cache, virtual memory,
channels.
Communication Theory
https://www.facebook.com/groups/govtcse.itjob/ https://www.facebook.com/duranta.ac
� Website: https://duranta.app/
Spectral analysis: Fourier series, sampling function, power spectrum, Fourier transform,
convolution, Parseval ‘s theorem; Information theory: entropy, information rate, Shannon ‘s
theorem, channel capacity; Analog communication system: different modulations, modulation
circuits and detectors; Digital modulation: different standard modulation schemes; Pulse and
digital signals: pulse amplitude modulation (PAM), pulse code modulation (PCM), delta
modulation (DM), adaptive delta modulation (ADM); Multiplexing: time-division multiplexing
(TDM) frequency-division multiplexing (FDM), multiple-access network- time-division
multiple-access (TDMA), frequency-division multiple access (FDMA); code division multiple-
access (CDMA).
Computer Networking and Security
Protocol hierarchies; Data link control: HLDC; DLL in Internet; DLL of ATM; LAN Protocols:
Standards IEEE 802.*; Hubs, Bridges, and Switches, FDDI, Fast Ethernet; Routing algorithm;
Congestion control; Internetworking, WAN; Fragmentation; Firewalls; IPV4, IPV6, ARP,
RARP, Mobile IP, Network layer of ATM; Transport protocols; Transmission control protocol:
connection management, transmission policy, congestion control, timer management; UDP;
AAL of ATM; Network security: Cryptography, DES, IDEA, public key algorithm;
Authentication; Digital signatures; Gigabit Ethernet; Domain Name System: Name servers;
Email and its privacy; SNMP; HTTP; World Wide Web.
Programming Language
Structured programming language: data types, operators, expressions, control structures;
Functions and program structure: parameter passing conventions, scope rules and storage classes,
recursion; Header files; Preprocessor; Pointers and arrays; Strings; Multidimensional array; User
defined data types: structures, unions, enumerations; Input and Output: standard input and
output, formatted input and output, file access; Variable length argument list; Command line
parameters; Error Handling; Graphics; Linking; Library functions. Object Oriented Programing
language: Philosophy of Object Oriented Programming (OOP); Advantages of OOP over
structured programming; Encapsulation, classes and objects, access specifiers, static and
nonstatic members; Constructors, destructors and copy constructors; Array of objects, object
pointers, and object references; Inheritance: single and multiple inheritance; Polymorphism:
overloading, abstract classes, virtual functions and overriding; Exceptions; Object Oriented I/O;
Template functions and classes; Multithreaded Programming. Theory: Discrete Mathematics,
Theory of Computation and Basic Graph Theory Set theory; Relations; Functions; Graph theory;
Propositional calculus and predicate calculus; Mathematical reasoning: induction, contradiction
and recursion; counting; Principles of inclusion and exclusion; Recurrence relations; Algebraic
structures: rings and groups. Graphs: simple graphs, digraphs, subgraphs, vertex-degrees, walks,
paths and cycles; Trees, spanning trees in graphs, distance in graphs; Complementary graphs,
cut-vertices, bridges and blocks, k-connected graphs;
https://www.facebook.com/groups/govtcse.itjob/ https://www.facebook.com/duranta.ac
� Website: https://duranta.app/
Theory of Computation: Language theory; Finite automata: deterministic finite automata,
nondeterministic finite automata, equivalence and conversion of deterministic and
nondeterministic finite automata, pushdown automata; Context free languages; Context free
grammars; Turing Machines: basic machines, configuration, computing with Turing machines
Data Structures and Algorithms: Internal data representation; Abstract data types; Elementary
data structures: arrays, lists, stacks, queues, trees, graphs; Advanced data Structures: heaps,
Fibonacci heaps, B-trees; Recursion, sorting, searching, hashing, storage management.
Techniques for analysis of algorithms; Methods for the design of efficient algorithms: divide and
conquer, greedy method, dynamic programming, back tracking, branch and bound; Basic search
and traversal techniques; Topological sorting; Connected components, spanning trees, shortest
paths; Flow algorithms;
Approximation algorithms; Parallel algorithms; Algebraic simplification and transformations;
Lower bound theory; NP-completeness, NP-hard and NP-complete problems.
Database Systems: Concepts of database systems; Data Models: Entity-Relationship model,
Relational model; Query Languages: Relational algebra, SQL; Constraints and triggers;
Functional dependencies and normalization; File organization and data storage; Indexing:
primary and secondary indexes, B+ trees, hash tables; Query optimization; Transaction
management; Recovery; Concurrency control; Access control and security; Semi structured
database: XML, XPath, XQuery; Object oriented and object relational databases.
Software Engineering and Information System Design: Concepts of Software Engineering,
Software Engineering paradigms, Different phases of software System Development, Different
types of information, qualities of information. Project Management Concepts, Software process
and project Metrics, Software Project Planning, Risk Analysis and management, Project
Scheduling and Tracking. Analysis Concepts and principles: requirement analysis, Analysis
modeling, data modeling. Design concepts and principles, Architectural design, User Interface
design, Object Oriented software development and design: Iterative Development and the
Unified Process. Sequential waterfall life cycles, Inception. Use case model for requirement
writing, Elaboration using System Sequence Diagram, Domain Model. Visualizing concept
classes. UML diagrams, Interaction and Collaboration Diagram for designing Software.
Designing Objects with responsibilities. GRASP patterns with General Principles in assigning
responsibilities: Information expert, Creator, Low Coupling and High Cohesion, Creating design
class diagrams and mapping design to codes. Software Testing: White Box and Black Box
testing. Basis Path Testing. Testing for specialized environment. Software testing strategies: Unit
Testing, Integration Testing, Validation Testing, System Testing, Art of debugging. Analysis of
System Maintenance and upgrading: Software repair, downtime, error and faults, specification
and correction, Maintenance cost models, documentation. Software Quality Assurance, Quality
factors. Software quality measures. Cost impact of Software defects. Concepts of Software
https://www.facebook.com/groups/govtcse.itjob/ https://www.facebook.com/duranta.ac
� Website: https://duranta.app/
reliability, availability and safety. Function based metrics and bang metrics. Metrics for analysis
and design model. Metrics for source code, testing and maintenance
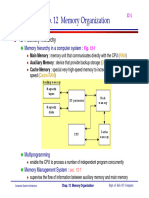
Operating System
Operating System: its role in computer systems; Operating system concepts; Operating system
structure; Process: process model and implementation, Inter-Process Communication (IPC),
classical IPC problems, process scheduling, multiprocessing and time-sharing; Memory
management: swapping, paging, segmentation, virtual memory; Input/Output: hardware,
software, disk, terminals, clocks; Deadlock: resource allocation and deadlock, deadlock
detection, prevention and recovery; File Systems: files, directories, security, protection; Case
study of some operating systems.
Artificial Intelligence
Introduction to old and new AI techniques; Knowledge representation; Propositional and first
order logic; Search techniques in AI; Probabilistic reasoning; Natural language processing.
Introduction to expert system. Introduction to machine learning; Learning algorithms: supervised
and unsupervised; Practical application of machine learning; Regression; Clustering.
References: BPSC Website – BCS Written Syllabus
https://www.facebook.com/groups/govtcse.itjob/ https://www.facebook.com/duranta.ac