0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views9 pagesModes of Transfer
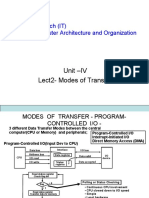
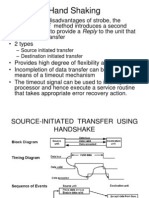
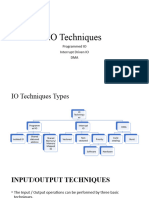
The document discusses different modes of data transfer in computer architecture, including Programmed I/O, Interrupt Initiated I/O, and Direct Memory Access (DMA). Programmed I/O requires constant CPU monitoring, while Interrupt Initiated I/O allows the CPU to perform other tasks until an interrupt signals data readiness. DMA enables high-speed data transfer between I/O devices and memory with minimal CPU involvement, improving efficiency and responsiveness in multitasking environments.
Uploaded by
gnesacme24Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views9 pagesModes of Transfer
The document discusses different modes of data transfer in computer architecture, including Programmed I/O, Interrupt Initiated I/O, and Direct Memory Access (DMA). Programmed I/O requires constant CPU monitoring, while Interrupt Initiated I/O allows the CPU to perform other tasks until an interrupt signals data readiness. DMA enables high-speed data transfer between I/O devices and memory with minimal CPU involvement, improving efficiency and responsiveness in multitasking environments.
Uploaded by
gnesacme24Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 9