0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesDrop Database If Exists Sample2
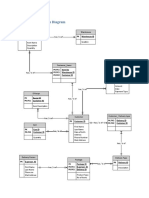
The document outlines the creation of a MySQL database named 'sample2' with two tables: 'customer' and 'customer_orders'. It includes the definition of the tables, their columns, and constraints, along with several SQL commands to insert records into these tables. Additionally, it demonstrates the use of default values and foreign key relationships between the tables.
Uploaded by
umaisalima62Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesDrop Database If Exists Sample2
The document outlines the creation of a MySQL database named 'sample2' with two tables: 'customer' and 'customer_orders'. It includes the definition of the tables, their columns, and constraints, along with several SQL commands to insert records into these tables. Additionally, it demonstrates the use of default values and foreign key relationships between the tables.
Uploaded by
umaisalima62Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3