0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views10 pagesIntegration 1
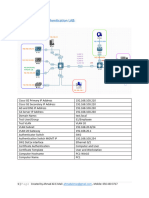
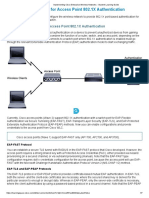
The document outlines the configuration steps necessary for integrating Cisco ISE with network switches and wireless controllers, including enabling web authentication, configuring RADIUS, and setting up AAA functions. It details commands for device tracking, DHCP snooping, and VLAN definitions to enhance security and authentication methods like 802.1X and MAB. Additionally, it provides guidelines for configuring wireless controllers to support iOS devices and setting up ACLs for device management interoperability.
Uploaded by
Seymur MammadovCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views10 pagesIntegration 1
The document outlines the configuration steps necessary for integrating Cisco ISE with network switches and wireless controllers, including enabling web authentication, configuring RADIUS, and setting up AAA functions. It details commands for device tracking, DHCP snooping, and VLAN definitions to enhance security and authentication methods like 802.1X and MAB. Additionally, it provides guidelines for configuring wireless controllers to support iOS devices and setting up ACLs for device management interoperability.
Uploaded by
Seymur MammadovCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10