0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views21 pagesArchitecture ATmega328 Microcontroller - 26march
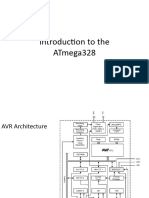
The document provides an overview of the ATmega328P microcontroller, detailing its architecture, features, and components including RAM, ROM, EEPROM, and clock speed. It highlights the microcontroller's specifications such as memory capacity, power supply requirements, and pin configurations, as well as its applications in embedded systems. Additionally, it compares the ATmega328P with the ATmega2560 microcontroller, noting differences in I/O pins, memory, and other specifications.
Uploaded by
kkp002003Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views21 pagesArchitecture ATmega328 Microcontroller - 26march
The document provides an overview of the ATmega328P microcontroller, detailing its architecture, features, and components including RAM, ROM, EEPROM, and clock speed. It highlights the microcontroller's specifications such as memory capacity, power supply requirements, and pin configurations, as well as its applications in embedded systems. Additionally, it compares the ATmega328P with the ATmega2560 microcontroller, noting differences in I/O pins, memory, and other specifications.
Uploaded by
kkp002003Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 21