Modular Design
What Is a Module?
• The term “module” refers to the design
and/or implementation of specific
functionality to be incorporated into a
program.
�Advantages of Modular Programming
� Module Specification
• Every module needs to provide a specification of
how it is to be used. This is referred to as the
module’s interface .
• Any program code making use of a particular
module is referred to as a client of the module.
• A module’s specification should be sufficiently
clear and complete so that its clients can
effectively utilize it.
• For example, numPrimes is a function that returns
the number of primes in a given integer range
��• The function’s specification is provided by the line immediately
following the function header, called a docstring in Python.
• A docstring is a string literal denoted by triple quotes given as the
first line of certain program elements.
• The docstring of a particular program element can be displayed by
use of the __doc__ extension,
• >>> print(numPrimes.__doc__)
• Returns the number of primes between start and end.
• This provides a convenient way for discovering how to use a
particular function without having to look at the function
definition itself.
• Some software development tools also make use of docstrings.
��• This docstring follows the Python convention
of putting a blank line after the first line of the
docstring, which should be an overall
description of what the function does,
followed by an arbitrary number of lines
providing additional details.
• These additional lines must be indented at the
same level, as shown in the figure.
�• A module’s interface is a specification of what
it provides and how it is to be used. Any
program code making use of a given module is
called a client of the module.
• A docstring is a string literal denoted by triple
quotes used in Python for providing the
specification of certain program elements.
� Top-Down Design
• Top-down design is an approach for deriving
a modular design in which the overall design
of a system is developed first, deferring the
specification of more detailed aspects of the
design until later steps.
• The goal of top-down design is that each
module provides clearly defined functionality,
which collectively provide all of the required
functionality of the program.
�First Stage of a Modular Design of the
Calendar Year Program
�Second Stage of Modular Design of a
Calendar Year Program
��� Python Modules
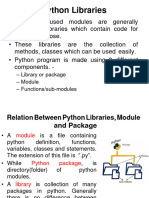
• What Is a Python Module?
• A Python module is a file containing Python
definitions and statements.
• The Python Standard Library contains a set of
predefined standard (built-in) modules.
�• Create a Python module by entering the following in a file name
simple.py. Then execute the instructions in the Python shell as
shown and observe the results.
• # module simple
print('module simple loaded')
def func1():
print('func1 called')
def func2():
print('func2 called')
• >>> import simple
• ???
• >>> simple.func1()
• ???
• >>> simple.func2()
• ???
� Modules and Namespaces
• A namespace provides a context for a set of
identifiers.
• Every module in Python has its own
namespace.
• A name clash is when two otherwise distinct
entities with the same identifier become part
of the same scope.
���• Enter each of the following functions in their own modules
named mod1.py and mod2.py. Enter and execute the
following and observe the results.
# mod1
def average(lst):
print('average of mod1 called')
# mod2
def average(lst):
print('average of mod1 called')
>>>import mod1, mod2
>>> mod1.average([10, 20, 30])
???
>>> mod2.average([10, 20, 30])
???
>>> average([10, 20, 30])
� Importing Modules
• In Python, the main module of any program is
identified as the first (“top-level”) module
executed.
� The “import modulename ” Form of
Import
• With the import modulename form of import
in Python, the namespace of the imported
module becomes available to, but does not
become part of, the namespace of the
importing module.
• Example
>>>Import math
>>>Factorial(5)
�The “from-import” Form of Import
• Python also provides an alternate import
statement of the form
from modulename import something
• where something can be a list of identifiers, a
single renamed identifier, or an asterisk, as shown
• below,
• (a) from modulename import func1, func2
• (b) from modulename import func1 as
new_func1
• (c) from modulename import *
�• With the from-import form of import,
imported identifiers become part of the
importing module’s namespace. Because of
the possibility of name clashes, import
modulename is the preferred form of import
in Python.
� Module Private Variables
• In Python, all the variables in a module are
“public,” with the convention that variables
beginning with an two underscores are
intended to be private.