0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views6 pages? What Is An API in IoT
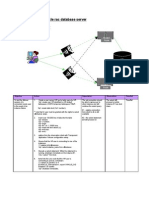
APIs in IoT facilitate communication between devices and applications, enabling functions such as data transmission, remote control, and cloud integration. Various types of APIs, including REST, MQTT, and CoAP, serve different communication needs in IoT environments. Communication models like Device-to-Device and Device-to-Cloud define how data flows between devices and services, while APIs provide the specific methods for executing these interactions.
Uploaded by
satyaprasadmohanty5Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views6 pages? What Is An API in IoT
APIs in IoT facilitate communication between devices and applications, enabling functions such as data transmission, remote control, and cloud integration. Various types of APIs, including REST, MQTT, and CoAP, serve different communication needs in IoT environments. Communication models like Device-to-Device and Device-to-Cloud define how data flows between devices and services, while APIs provide the specific methods for executing these interactions.
Uploaded by
satyaprasadmohanty5Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6