0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageGetting Started With FL Studio
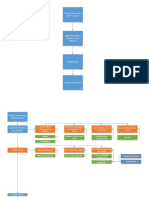
FL Studio is a widely-used digital audio workstation that enables beginners to create professional-quality music through its user-friendly interface and powerful features. Key components include the Channel Rack for sequencing, the Piano Roll for composing melodies, the Playlist for arranging songs, and the Mixer for controlling audio effects. Beginners are encouraged to start with simple projects and utilize online resources to enhance their learning and creativity.
Uploaded by
casijef413Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageGetting Started With FL Studio
FL Studio is a widely-used digital audio workstation that enables beginners to create professional-quality music through its user-friendly interface and powerful features. Key components include the Channel Rack for sequencing, the Piano Roll for composing melodies, the Playlist for arranging songs, and the Mixer for controlling audio effects. Beginners are encouraged to start with simple projects and utilize online resources to enhance their learning and creativity.
Uploaded by
casijef413Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 1