0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesModbus Function Code and Address Range
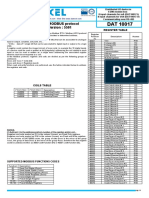
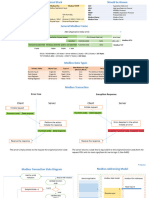
The document outlines the object types and access methods for a Modbus slave device, detailing coils, discrete inputs, input registers, and holding registers. It lists the most commonly used function codes for reading and writing these objects, along with their corresponding address ranges. Additionally, it provides a formula for calculating the DCS address from the PLC address.
Uploaded by
vdevnikhilCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesModbus Function Code and Address Range
The document outlines the object types and access methods for a Modbus slave device, detailing coils, discrete inputs, input registers, and holding registers. It lists the most commonly used function codes for reading and writing these objects, along with their corresponding address ranges. Additionally, it provides a formula for calculating the DCS address from the PLC address.
Uploaded by
vdevnikhilCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3