0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views26 pagesExcel For Data Analysts
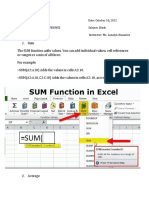
Microsoft Excel is a versatile spreadsheet application used for data analysis, organization, and visualization, featuring tools like formulas, charts, pivot tables, and conditional formatting. Key functionalities include data manipulation techniques such as sorting, filtering, and grouping, as well as data visualization options like charts and sparklines. Excel also supports collaboration and offers various formatting tools to enhance the presentation of data.
Uploaded by
rohtakiya124001Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views26 pagesExcel For Data Analysts
Microsoft Excel is a versatile spreadsheet application used for data analysis, organization, and visualization, featuring tools like formulas, charts, pivot tables, and conditional formatting. Key functionalities include data manipulation techniques such as sorting, filtering, and grouping, as well as data visualization options like charts and sparklines. Excel also supports collaboration and offers various formatting tools to enhance the presentation of data.
Uploaded by
rohtakiya124001Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 26