0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesArray Application Best Usage
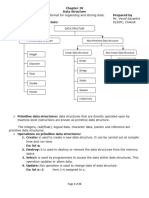
An array is a fundamental data structure that stores elements in contiguous memory locations, allowing for efficient access via indexing. Key characteristics include being indexed, containing homogeneous elements, and having a fixed size in static arrays, while dynamic arrays provide resizing capabilities. Arrays offer advantages like fast access and cache locality but have disadvantages such as fixed size and slow insertions and deletions, making them suitable for various applications like stacks, queues, and image processing.
Uploaded by
ztt15384Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesArray Application Best Usage
An array is a fundamental data structure that stores elements in contiguous memory locations, allowing for efficient access via indexing. Key characteristics include being indexed, containing homogeneous elements, and having a fixed size in static arrays, while dynamic arrays provide resizing capabilities. Arrays offer advantages like fast access and cache locality but have disadvantages such as fixed size and slow insertions and deletions, making them suitable for various applications like stacks, queues, and image processing.
Uploaded by
ztt15384Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2