0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesLab 11 - Tree
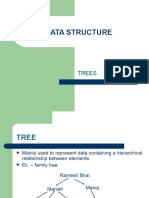
The document outlines the objectives and tasks for Lab 11 of the Data Structures and Algorithms course, focusing on tree data structures. Students will implement binary trees using both linked and array-based representations, analyzing the advantages and disadvantages of each approach. The lab includes specific tasks with requirements for implementing various functions in both representations, along with guidelines for a main program to test the implementations.
Uploaded by
Mudasar IqbalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesLab 11 - Tree
The document outlines the objectives and tasks for Lab 11 of the Data Structures and Algorithms course, focusing on tree data structures. Students will implement binary trees using both linked and array-based representations, analyzing the advantages and disadvantages of each approach. The lab includes specific tasks with requirements for implementing various functions in both representations, along with guidelines for a main program to test the implementations.
Uploaded by
Mudasar IqbalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2