0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesMatlab Code
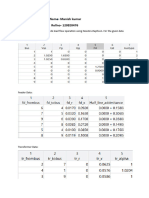
The MATLAB code calculates and displays symmetrical components of phase currents and voltages based on given inputs. It transforms the phase values into complex phasors, computes the sequence components, and presents the results in a table format. Additionally, it generates phasor diagrams for phase currents, phase voltages, sequence currents, and sequence voltages.
Uploaded by
irtiza.cu.cuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesMatlab Code
The MATLAB code calculates and displays symmetrical components of phase currents and voltages based on given inputs. It transforms the phase values into complex phasors, computes the sequence components, and presents the results in a table format. Additionally, it generates phasor diagrams for phase currents, phase voltages, sequence currents, and sequence voltages.
Uploaded by
irtiza.cu.cuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3