0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views8 pagesNetworking Notes 6AB
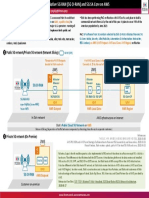
The document covers key concepts in computer science, focusing on networks, data transmission, and programming in Python. It explains subroutines, network security, encryption, and how URLs and IP addresses work, along with the basics of Python syntax, data types, and common errors. Additionally, it includes a case study on creating a simple program to add two numbers.
Uploaded by
nagpalsanjna1Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views8 pagesNetworking Notes 6AB
The document covers key concepts in computer science, focusing on networks, data transmission, and programming in Python. It explains subroutines, network security, encryption, and how URLs and IP addresses work, along with the basics of Python syntax, data types, and common errors. Additionally, it includes a case study on creating a simple program to add two numbers.
Uploaded by
nagpalsanjna1Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 8