0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views4 pagesData Type - Javatpoint
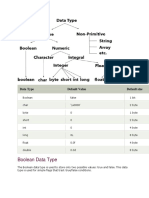
The document explains data types in VB.NET, detailing their definitions, syntax, and the memory space they occupy. It includes examples of using various data types in a program and describes type conversion functions available in VB.NET. Additionally, it highlights the importance of 'Option Strict On' for data type conversion, which can restrict certain conversions.
Uploaded by
PHẠM HỮU ÁICopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views4 pagesData Type - Javatpoint
The document explains data types in VB.NET, detailing their definitions, syntax, and the memory space they occupy. It includes examples of using various data types in a program and describes type conversion functions available in VB.NET. Additionally, it highlights the importance of 'Option Strict On' for data type conversion, which can restrict certain conversions.
Uploaded by
PHẠM HỮU ÁICopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4