12/21/23, 2:30 PM CPU Architecture
CPU Architecture
Microprocessing unit is synonymous to central processing unit, CPU used in
traditional computer. Microprocessor (MPU) acts as a device or a group of devices
which do the following tasks.
communicate with peripherals devices
provide timing signal
direct data flow
perform computer tasks as specified by the instructions in memory
8085 Microprocessor
The 8085 microprocessor is an 8-bit general purpose microprocessor which is
capable to address 64k of memory. This processor has forty pins, requires +5 V
single power supply and a 3-MHz single-phase clock.
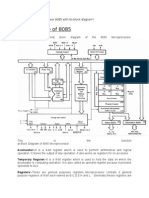
Block Diagram
ALU
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/cpu_architecture.htm 1/6
�12/21/23, 2:30 PM CPU Architecture
The ALU perform the computing function of microprocessor. It includes the
accumulator, temporary register, arithmetic & logic circuit & and five flags. Result is
stored in accumulator & flags.
Block Diagram
Accumulator
It is an 8-bit register that is part of ALU. This register is used to store 8-bit data & in
performing arithmetic & logic operation. The result of operation is stored in
accumulator.
Diagram
Flags
Flags are programmable. They can be used to store and transfer the data from the
registers by using instruction. The ALU includes five flip-flops that are set and reset
according to data condition in accumulator and other registers.
S (Sign) flag − After the execution of an arithmetic operation, if bit D7 of
the result is 1, the sign flag is set. It is used to signed number. In a given
byte, if D7 is 1 means negative number. If it is zero means it is a positive
number.
Z (Zero) flag − The zero flag is set if ALU operation result is 0.
AC (Auxiliary Carry) flag − In arithmetic operation, when carry is
generated by digit D3 and passed on to digit D4, the AC flag is set. This flag is
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/cpu_architecture.htm 2/6
�12/21/23, 2:30 PM CPU Architecture
used only internally BCD operation.
P (Parity) flag − After arithmetic or logic operation, if result has even
number of 1s, the flag is set. If it has odd number of 1s, flag is reset.
C (Carry) flag − If arithmetic operation result is in a carry, the carry flag is
set, otherwise it is reset.
Register section
It is basically a storage device and transfers data from registers by using
instructions.
Stack Pointer (SP) − The stack pointer is also a 16-bit register which is
used as a memory pointer. It points to a memory location in Read/Write
memory known as stack. In between execution of program, sometime data to
be stored in stack. The beginning of the stack is defined by loading a 16-bit
address in the stack pointer.
Program Counter (PC) − This 16-bit register deals with fourth operation to
sequence the execution of instruction. This register is also a memory pointer.
Memory location have 16-bit address. It is used to store the execution
address. The function of the program counter is to point to memory address
from which next byte is to be fetched.
Storage registers − These registers store 8-bit data during a program
execution. These registers are identified as B, C, D, E, H, L. They can be
combined as register pair BC, DE and HL to perform some 16 bit operations.
Time and Control Section
This unit is responsible to synchronize Microprocessor operation as per the clock
pulse and to generate the control signals which are necessary for smooth
communication between Microprocessor and peripherals devices. The RD bar and WR
bar signals are synchronous pulses which indicates whether data is available on the
data bus or not. The control unit is responsible to control the flow of data between
microprocessor, memory and peripheral devices.
PIN diagram
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/cpu_architecture.htm 3/6
�12/21/23, 2:30 PM CPU Architecture
All the signal can be classified into six groups
Instruction Format
Each instruction is represented by a sequence of bits within the computer. The
instruction is divided into group of bits called field. The way instruction is expressed
is known as instruction format. It is usually represented in the form of rectangular
box. The instruction format may be of the following types.
Variable Instruction Formats
These are the instruction formats in which the instruction length varies on the basis
of opcode & address specifiers. For Example, VAX instruction vary between 1 and 53
bytes while X86 instruction vary between 1 and 17 bytes.
Format
Advantage
These formats have good code density.
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/cpu_architecture.htm 4/6
�12/21/23, 2:30 PM CPU Architecture
Drawback
These instruction formats are very difficult to decode and pipeline.
Fixed Instruction Formats
In this type of instruction format, all instructions are of same size. For Example,
MIPS, Power PC, Alpha, ARM.
Format
Advantage
They are easy to decode & pipeline.
Drawback
They don't have good code density.
Hybrid Instruction Formats
In this type of instruction formats, we have multiple format length specified by
opcode. For example, IBM 360/70, MIPS 16, Thumb.
Format
Advantage
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/cpu_architecture.htm 5/6
�12/21/23, 2:30 PM CPU Architecture
These compromise between code density & instruction of these type are very easy to
decode.
Addressing Modes
Addressing mode provides different ways for accessing an address to given data to a
processor. Operated data is stored in the memory location, each instruction required
certain data on which it has to operate. There are various techniques to specify
address of data. These techniques are called Addressing Modes.
Direct addressing mode − In the direct addressing mode, address of the
operand is given in the instruction and data is available in the memory
location which is provided in instruction. We will move this data in desired
location.
Indirect addressing mode − In the indirect addressing mode, the
instruction specifies a register which contain the address of the operand. Both
internal RAM and external RAM can be accessed via indirect addressing mode.
Immediate addressing mode − In the immediate addressing mode, direct
data is given in the operand which move the data in accumulator. It is very
fast.
Relative addressing mode − In the relative address mode, the effective
address is determined by the index mode by using the program counter in
stead of general purpose processor register. This mode is called relative
address mode.
Index addressing mode − In the index address mode, the effective address
of the operand is generated by adding a content value to the contents of the
register. This mode is called index address mode.
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/cpu_architecture.htm 6/6