0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views14 pagesWhat Is A Computer
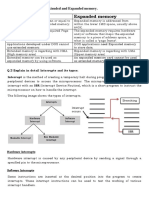
A computer is an electronic device that processes and executes instructions to perform tasks, utilizing components such as the CPU, RAM, and storage. It operates based on binary code and can be categorized into various types, including desktops, laptops, and servers, with a rich history dating back to the abacus. Computers offer advantages like increased efficiency and access to information, but also pose challenges such as security risks and job displacement.
Uploaded by
5mvr8z2j8yCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views14 pagesWhat Is A Computer
A computer is an electronic device that processes and executes instructions to perform tasks, utilizing components such as the CPU, RAM, and storage. It operates based on binary code and can be categorized into various types, including desktops, laptops, and servers, with a rich history dating back to the abacus. Computers offer advantages like increased efficiency and access to information, but also pose challenges such as security risks and job displacement.
Uploaded by
5mvr8z2j8yCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 14