0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views26 pagesDSA Lab Report Lab 3final
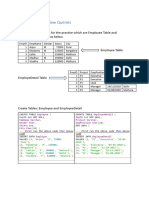
The document outlines a lab session focused on fundamental data structures, specifically arrays and linked lists, with practical applications. It includes tasks such as creating a student record management system using arrays, implementing basic image processing with 2D arrays, designing a to-do list manager with a singly linked list, and creating a music playlist application using a doubly linked list. Each task involves specific programming requirements and memory management considerations.
Uploaded by
Abdullah ShaheerCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views26 pagesDSA Lab Report Lab 3final
The document outlines a lab session focused on fundamental data structures, specifically arrays and linked lists, with practical applications. It includes tasks such as creating a student record management system using arrays, implementing basic image processing with 2D arrays, designing a to-do list manager with a singly linked list, and creating a music playlist application using a doubly linked list. Each task involves specific programming requirements and memory management considerations.
Uploaded by
Abdullah ShaheerCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 26