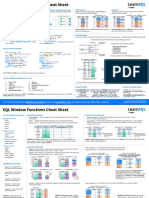
What Are Window Functions?
Window functions let you do calculations on a group of rows (a window) that are
related to the current row — without collapsing the data like GROUP BY does. They
work row by row, but let you look at data around each row.
Basic Structure of a Window Function:
SYNTAX :-
FUNCTION_NAME() OVER (
PARTITION BY column
ORDER BY column
ROWS BETWEEN ... AND ...
)
___________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________
1. Ranking Functions
These assign a number (rank) to each row based on order.
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------+
Function | What it does | Simple
meaning
ROW_NUMBER() | Gives each row a unique number in order. | "Count each
row in order."
RANK() | Gives same rank to ties, skips next ranks. | "Ties
get same rank, then jumps."
DENSE_RANK() | Like RANK(), but no skips after ties. | "Ties
get same rank, no jump."
NTILE(n) | Divides rows into n equal parts. | "Put rows into
buckets."
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------+
example :
SELECT name, salary, RANK() OVER (ORDER BY salary DESC) AS salary_rank
FROM employees;
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------
2. Aggregate Functions (used as window functions)
Normally used with GROUP BY, but here they calculate over a window, not collapse
rows.
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
----+
Function | What it does
SUM() | Adds values over the window
AVG() | Averages values
COUNT() | Counts rows in the window
MIN() / MAX() | Finds smallest/largest value
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
----+
example:
SELECT name, dept, salary, AVG(salary) OVER (PARTITION BY dept) AS
avg_salary_in_dept
FROM employees;
�-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------
3. Value Functions
They let you look at other rows (previous, next, etc.) from the current row's point
of view.
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
----+
Function | What it does | Use
LAG() | Gets value from a previous row | Compare past value
LEAD() | Gets value from a next row | Look ahead
FIRST_VALUE() | First row in window | Get starting point
LAST_VALUE() | Last row in window | Get ending point
NTH_VALUE(n) | nth row in window | Pick specific position
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
----+
example:
SELECT name, salary, LAG(salary) OVER (ORDER BY id) AS prev_salary
FROM employees;
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------
4. Window Frame Functions
These control which rows in the window to include, usually used with aggregates.
ROWS BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW
= from the start to current row
ROWS BETWEEN 1 PRECEDING AND 1 FOLLOWING
= 1 row before and after the current row
example:
SELECT name, salary, UM(salary) OVER (ORDER BY id ROWS BETWEEN 1 PRECEDING AND 1
FOLLOWING) AS moving_sum
FROM employees;