Experiment - 1
KHATRA VIVEK RANIKBHAI - EE23BT052
NAKKA SHEETAL RAO - EE23BT051
Objectives of the Experiment
AIM: The primary aim of this experiment is to perform open circuit (OC) and short circuit (SC) tests on
a single-phase transformer. The specific objectives are:
• To predetermine the efficiency and voltage regulation of the transformer.
• To develop the equivalent circuit of the transformer.
Summary
The performance of large power transformers cannot be easily determined by a direct load test due to the
immense energy waste and the difficulty in obtaining a suitable large load. Therefore, the performance is
computed from the knowledge of its losses and equivalent circuit parameters, which are determined from the
OC and SC tests. The OC test measures the no-load losses (iron losses) and determines the magnetizing
branch parameters (R0 and X0 ), while the SC test measures the full-load copper losses and determines the
equivalent resistance and reactance of the windings (R01 and X01 ).
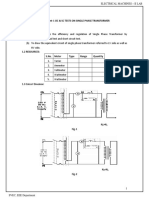
Circuit Diagram
The circuit diagrams for both the Open Circuit and Short Circuit tests are provided below, as specified in
the lab manual.
Figure 1: Open Circuit Test Circuit Diagram (Top);
Figure 2: Short Circuit Test Circuit Diagram (Bottom)
1
�Experimental Set up Details
Transformer Name Plate Details:
• Transformer Rating: 115/230 V, 1 KVA
• LV Voltage: 115 V
• HV Voltage: 230 V
Apparatus Required
The following apparatus is required for the experiment, with ranges and types to be filled in from the lab
equipment.
S.No Apparatus Range or Rating Type Qty
1. Ammeter 0-1 A AC 1
2. Ammeter 0-5 A AC 1
3. Voltmeter 0-150 V AC 1
4. Voltmeter 0-300 V AC 1
5. Wattmeter 150V , 1A, 150W UPF 1
6. Wattmeter 300V , 5A, 750W LP F 1
7. Auto transformer 1-Φ, 230V, 50Hz V ariableAutotransf ormer 1
Observation and Calculations
Open Circuit Test
Procedure: 1. Make the connections as shown in the Open Circuit Test diagram (Fig 1).
2. Ensure the secondary (HV) side of the transformer is open-circuited.
3. Set the autotransformer to zero output voltage.
4. Gradually increase the voltage until the voltmeter reads the rated voltage of the LV winding (115V).
5. Note the readings of the voltmeter, ammeter, and wattmeter. The wattmeter reading gives the iron losses
(W0 ).
S. NO Voltage(V) Current(I) W0 (Watts)
Observation Table:
1 115 3.6 13.6
Sample Calculations: The no-load equivalent circuit parameters are calculated as follows:
• Power Factor: Cos ϕo = W0
V0 I0 = 0.32
• Magnetizing Current: Im = Io Sin ϕo = 3.5A
• Core Loss Current: Ic = Io Cos ϕo = 0.115A
• Core Loss Resistance: Rc = Vo
Ic = 1000Ω
• Magnetizing Reactance: Xm = Vo
Im = 32.85Ω
Short Circuit Test
Procedure: 1. Make the connections as shown in the Short Circuit Test diagram (Fig 2).
2. Short-circuit the LV winding.
3. Apply a very low voltage (5-8% of rated voltage) to the HV winding using the autotransformer.
4. Slowly increase the voltage until the ammeter reads the rated full-load current.
5. Note the readings of the voltmeter, ammeter, and wattmeter. The wattmeter reading gives the full-load
copper losses (Wsc ).
Voltmeter (Vsc ) Ammeter (Isc ) Wattmeter(Wsc )
Observation Table:
45 4.3 160
Sample Calculations: The equivalent impedance, resistance, and reactance referred to the HV side are
calculated as follows:
2
� • Equivalent Impedance: Zsc = VSC
ISc = 10.46Ω
• Equivalent Resistance: Req2 = WSC
2
ISC
= 8.65Ω
q
• Equivalent Reactance: Xeq2 = 2 − R2
Zsc eq2 = 5.88Ω
Efficiency and Regulation
Estimation of Efficiency: Efficiency is calculated using the following formula:
Output k · (KV A) · Cosϕ
η= =
Input k · (KV A) · Cosϕ + Wi + k 2 · Wc
= 82.17%
Where: k is the fraction of full load KVA.
Wi is the iron loss determined from the OC test.
Wc is the full-load copper loss determined from the SC test.
Voltage Regulation: Voltage regulation can be calculated using the parameters obtained from the SC
test. The formula for regulation is given by:
IF L · Req2 · Cosϕ + IF L · Xeq2 · Sinϕ
Regulation =
E2
= 19.73%
Where: IF L is the full load current referred to the HV side.
Req2 and Xeq2 are the equivalent resistance and reactance referred to the HV side.
E2 is the no-load voltage on the HV side.
Conclusions
This experiment successfully demonstrated the procedure for conducting Open Circuit and Short Circuit
tests on a single-phase transformer. By performing these tests, we were able to determine the transformer’s
equivalent circuit parameters, which allowed for the predetermination of its efficiency and voltage regulation
without the need for a direct load test. The results obtained confirm the theoretical principles that OC tests
provide iron losses, while SC tests provide copper losses.