0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesData Serialization
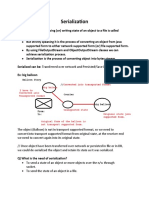
Data Serialization is the process of converting data structures into formats like JSON or XML for storage or transmission, while Deserialization reverses this process to reconstruct the original data. Serialization is crucial in microservices for cross-language communication, efficient network communication, and data storage. It is important to ensure secure practices during deserialization to prevent vulnerabilities.
Uploaded by
kamsjyo91Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesData Serialization
Data Serialization is the process of converting data structures into formats like JSON or XML for storage or transmission, while Deserialization reverses this process to reconstruct the original data. Serialization is crucial in microservices for cross-language communication, efficient network communication, and data storage. It is important to ensure secure practices during deserialization to prevent vulnerabilities.
Uploaded by
kamsjyo91Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2