0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views7 pagesTypes of Operating Systems
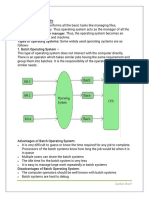
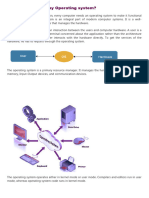
Operating systems can be categorized by their functionalities into eight main types: Batch, Multi-Programming, Multi-Processing, Multi-User, Distributed, Network, Real-Time, and Mobile Operating Systems. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, such as Batch systems managing jobs efficiently but having poor CPU utilization, while Real-Time systems are crucial for applications requiring strict time constraints. Mobile Operating Systems, like Android and iOS, are designed for mobile devices, offering user-friendly interfaces and extensive app ecosystems but facing challenges like battery life and security risks.
Uploaded by
ifraghaffar859Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views7 pagesTypes of Operating Systems
Operating systems can be categorized by their functionalities into eight main types: Batch, Multi-Programming, Multi-Processing, Multi-User, Distributed, Network, Real-Time, and Mobile Operating Systems. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, such as Batch systems managing jobs efficiently but having poor CPU utilization, while Real-Time systems are crucial for applications requiring strict time constraints. Mobile Operating Systems, like Android and iOS, are designed for mobile devices, offering user-friendly interfaces and extensive app ecosystems but facing challenges like battery life and security risks.
Uploaded by
ifraghaffar859Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 7