Q-15) What is communication? Explain the Data Transmission mode?
Ans:
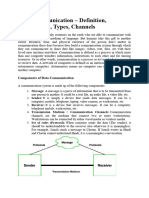
Communication is the exchange of information or data between two or more parties. It is an
essential process that is fundamental to human interaction and plays a vital role in personal and
professional relationships. Communication can take various forms, including verbal, written, or
electronic communication. In electronic communication, data transmission is the process of
transmitting data from one location to another using various communication channels, such as
wired or wireless networks.
There are three modes of data transmission, namely simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex. Each
mode has its unique characteristics and is used in different applications.
1. Simplex mode is the simplest mode of data transmission, where data transmission occurs in
only one direction. The sender transmits data to the receiver, and the receiver can only receive
the data; they cannot send data back to the sender. In this mode, the communication channel
is unidirectional, and the data transmission is one-way. The simplex mode is commonly used
in applications where the data transmission is one-way, and there is no need for the receiver
to send data back to the sender. For example, a radio broadcast is a simplex mode of
communication where the radio station broadcasts the signal, and the listeners can only
receive it.
2. Half-duplex mode is a mode of data transmission where data transmission can occur in both
directions, but not simultaneously. In this mode, the sender can transmit data to the receiver,
and once the transmission is complete, the receiver can send data back to the sender.
However, only one party can transmit at a time. In this mode, the communication channel is
bidirectional, and the data transmission is two-way, but not simultaneous. Half-duplex mode
is commonly used in applications where both parties need to communicate, but the data
transmission is not continuous. For example, a walkie-talkie is a half-duplex mode of
communication where one person can speak while the other person listens, and vice versa.
3. Full-duplex mode is the most advanced mode of data transmission, where data transmission
can occur in both directions simultaneously. In this mode, both the sender and receiver can
transmit data at the same time. The communication channel is bidirectional, and the data
transmission is two-way and simultaneous. Full-duplex mode is commonly used in
applications where continuous communication is required. For example, a telephone
conversation is a full-duplex mode of communication where both parties can talk and listen at
the same time.
�Q-16) Explain the categories of Data transmission Media?
Ans:
Data transmission media refer to the physical pathways or channels through which data is
transmitted from one location to another. There are three categories of data transmission media:
wired media, wireless media, and fiber optic media.
1. Wired Media: Wired media refers to physical pathways that use wires or cables to transmit
data. The most common types of wired media include coaxial cable, twisted pair cable, and fiber
optic cable.
- Coaxial Cable: Coaxial cable consists of a copper conductor surrounded by a layer of insulation,
which is in turn surrounded by a braided shield and an outer layer of insulation. Coaxial cable is
commonly used to transmit data over long distances, such as in cable TV and high-speed internet
connections.
- Twisted Pair Cable: Twisted pair cable consists of two copper wires twisted together and
surrounded by a layer of insulation. Twisted pair cable is commonly used in local area networks
(LANs) to connect computers and other devices.
- Fiber Optic Cable: Fiber optic cable consists of a thin strand of glass or plastic that transmits
data using light signals. Fiber optic cable is commonly used to transmit data over long distances,
such as in telecommunications networks.
2. Wireless Media: Wireless media refers to physical pathways that use wireless signals to
transmit data. The most common types of wireless media include radio waves, microwaves, and
infrared waves.
- Radio Waves: Radio waves are used to transmit data over long distances, such as in radio and
television broadcasting. Radio waves are also used in cellular phone networks.
- Microwaves: Microwaves are used to transmit data over short distances, such as in wireless
LANs. Microwaves are also used in satellite communications.
- Infrared Waves: Infrared waves are used to transmit data over short distances, such as in
remote controls and wireless keyboards. Infrared waves are also used in some wireless LANs.
3. fibres Optic Media: fibres optic media is a special type of wired media that uses fiber optic
cables to transmit data. fibre optic cables are made of thin strands of glass or plastic that
transmit data using light signals. Fibber optic media is commonly used in telecommunications
networks and high-speed internet connections.
Each type of data transmission media has its advantages and disadvantages. Wired media is
generally more reliable than wireless media, as it is not subject to interference from other
signals or environmental factors. Wired media is also more secure than wireless media, as it is
harder to intercept signals transmitted over a physical cable. However, wired media can be more
expensive to install and maintain than wireless media, as it requires physical cables to be
installed.
Wireless media is generally more convenient than wired media, as it allows for greater mobility
and flexibility. Wireless media is also less expensive to install and maintain than wired media, as
it does not require physical cables to be installed. However, wireless media is more susceptible
to interference from other signals and environmental factors, which can affect the quality of data
transmission.
Fiber optic media is a specialized type of wired media that offers higher bandwidth and greater
reliability than traditional wired media. Fiber optic media is capable of transmitting data over
longer distances than traditional wired media, and it is also less susceptible to interference.
However, fiber optic media can be more expensive to install and maintain than traditional wired
media, as it requires specialized equipment and expertise.
�Q-17) What is E- Communication & E- Collaboration?
Ans:
E-communication and e-collaboration are two closely related concepts that have emerged with
the rise of digital technologies and the internet. E-communication refers to the use of electronic
media to facilitate communication between individuals or groups, while e-collaboration refers to
the use of electronic tools to facilitate collaboration and teamwork.
E-communication:
E-communication includes various forms of electronic media, such as email, instant
messaging, video conferencing, and social media. These tools enable individuals to
communicate with each other in real-time or asynchronously, regardless of their location. E-
communication has revolutionized the way people communicate, making it faster, more
efficient, and more convenient than traditional communication methods.
Email is one of the most popular forms of e-communication. It allows individuals to send and
receive messages, documents, and other files quickly and easily. Instant messaging tools, such
as WhatsApp and Skype, enable real-time communication between individuals or groups,
which is particularly useful for informal communication and quick decision-making.
Video conferencing tools, such as Zoom and Microsoft Teams, enable individuals to hold
virtual meetings and conferences, regardless of their location. Social media platforms, such as
Facebook and Twitter, enable individuals to connect with each other and share information
and ideas on a global scale.
E-communication has numerous advantages, such as increased efficiency, speed, and
convenience. It enables individuals to communicate with each other instantly, regardless of
their location, and to share information and ideas quickly and easily. E-communication also
reduces the need for physical travel and face-to-face meetings, which can save time and
money.
E-collaboration:
E-collaboration refers to the use of electronic tools to facilitate collaboration and teamwork.
E-collaboration tools enable individuals to work together on projects and tasks, regardless of
their location. These tools can include project management software, document sharing
platforms, and virtual whiteboards.
Project management software, such as Asana and Trello, enable teams to manage tasks and
projects collaboratively, assigning tasks, setting deadlines, and tracking progress in real-time.
Document sharing platforms, such as Google Drive and Dropbox, enable teams to share and
collaborate on documents and files, ensuring that everyone has access to the latest version.
Virtual whiteboards, such as Miro and Lucid chart, enable teams to collaborate on
brainstorming sessions and visual ideation, allowing everyone to contribute ideas and
insights in real-time.
E-collaboration has numerous advantages, such as increased efficiency, improved
communication, and enhanced creativity. It enables teams to work together on projects and
tasks, regardless of their location, and to share information and ideas quickly and easily. E-
collaboration also enhances creativity by enabling teams to brainstorm and ideate
collaboratively, drawing on a diverse range of perspectives and insights.
�Q-18) What is CPU? Explain CU & ALU?
Ans:
CPU stands for Central Processing Unit, which is the main component of a computer system
responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations. It is often referred to as the
"brain" of the computer.
The CPU consists of two primary components: the Control Unit (CU) and the Arithmetic Logic
Unit (ALU).
Control Unit (CU):
The Control Unit is responsible for controlling the flow of data between the CPU and the other
components of the computer system, such as the memory and input/output devices. It
interprets the instructions fetched from memory and manages the execution of these
instructions. The CU also controls the sequence of operations within the CPU, ensuring that
instructions are executed in the correct order.
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU):
The Arithmetic Logic Unit is responsible for performing mathematical calculations and logical
operations. It performs arithmetic operations, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and
division, and logical operations, such as AND, OR, and NOT. The ALU uses registers to store data
and performs operations on these registers.
The CU and ALU work together to execute instructions and perform calculations. The CU fetches
instructions from memory and sends them to the ALU to be executed. The ALU performs the
necessary calculations and returns the result to the CU, which then sends the result to the
appropriate location in memory or to an output device.
In summary, the CPU is the central component of a computer system responsible for executing
instructions and performing calculations. It consists of two primary components: the Control
Unit (CU), which manages the flow of data and controls the sequence of operations, and the
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), which performs mathematical calculations and logical operations.
The CU and ALU work together to execute instructions and perform calculations, allowing the
computer to perform a wide range of tasks.
�Q-19) What is Worksheet? Explain the features of MS. Excel?
Ans:
A worksheet is a computer file or a virtual page within a spreadsheet application such as
Microsoft Excel. It is used to organize and manipulate data, perform calculations, and create
charts and graphs. A worksheet is comprised of rows and columns, and the intersection of a row
and a column is called a cell. Each cell can contain text, numbers, formulas, and other data.
Microsoft Excel is a powerful spreadsheet application that provides a wide range of features and
tools for managing and analysing data. Some of the key features of MS Excel are:
1. Spreadsheet Creation and Management:
MS Excel allows you to create and manage multiple spreadsheets within a single workbook. You
can add, delete, and rearrange worksheets, and copy and paste data between them. Excel also
allows you to easily format cells, rows, and columns, and adjust their size and alignment.
2. Data Entry and Manipulation:
Excel provides a variety of tools for entering and manipulating data. You can easily enter data
into cells, format it, and perform calculations using formulas and functions. Excel also provides
tools for sorting, filtering, and searching data, as well as for removing duplicates and validating
data.
3. Formulas and Functions:
Excel provides a wide range of formulas and functions for performing calculations. These
include basic arithmetic operators such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, as
well as more advanced functions such as statistical analysis, financial calculations, and data
manipulation.
4. Charting and Graphing:
Excel allows you to create a variety of charts and graphs based on your data. You can choose
from a range of chart types, including bar charts, line charts, and pie charts, and customize them
to suit your needs. Excel also provides tools for formatting charts, adding titles and labels, and
adjusting the data series.
5. Conditional Formatting:
Excel provides tools for formatting cells based on their values or other criteria. This is known as
conditional formatting. For example, you can highlight cells that contain a certain value, or
format cells based on the date or time.
6. Data Analysis:
Excel provides tools for analyzing data, such as pivot tables and data tables. Pivot tables allow
you to summarize and analyze large data sets, while data tables allow you to perform what-if
analysis and sensitivity analysis on your data.
7. Macros and Automation:
Excel provides tools for creating macros, which are sets of instructions that automate repetitive
tasks. You can use macros to perform complex calculations, format data, and automate other
tasks. Excel also provides tools for recording and editing macros, as well as for running macros
automatically.